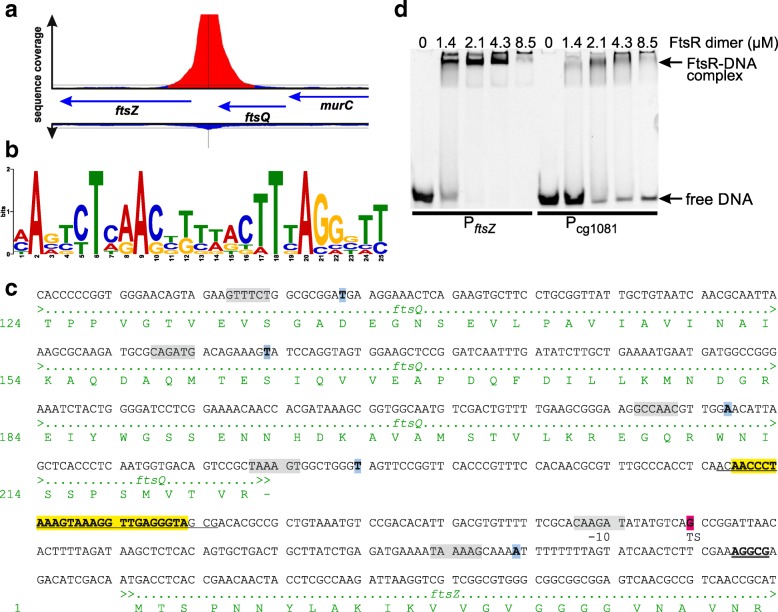
Fig. 5.
Binding of FtsR to the ftsZ promoter. a Enrichment of the ftsZ promoter region in the ChAP-Seq experiment with FtsR-Strep. The negative control is presented below the genes. b FtsR consensus DNA-binding motif identified by the MEME software [41] using the nine DNA regions with the highest coverage in the ChAP-Seq experiment with FtsR-Strep. c DNA sequence of the ftsZ promoter region including parts of the coding regions of ftsQ and ftsZ and the corresponding amino acid sequences. The ribosome binding site of ftsZ is double underlined. The transcriptional start site identified by RNA-Seq [29] in strain ATCC13032 is highlighted in magenta, the transcriptional start sites identified by primer extension and RACE in strain ATCC13689 [19] are indicated in blue. The deduced −10 regions are shown in grey boxes. The FtsR-binding site identified in this work is highlighted in yellow. The 30-bp region used for EMSAs with purified FtsR-Strep is underlined. d In vitro DNA-binding studies with FtsR-Strep. Purified FtsR-Strep was incubated in the indicated concentrations with a constant concentration (1 μM) of a 30-bp double-stranded oligonucleotide covering the predicted FtsR-binding site in the ftsZ-promoter region. The mixture was then analyzed by electrophoresis using a non-denaturing 15% (w/v) polyacrylamide gel. As negative control, a DNA fragment of the promoter region of cg1081 was used (1 μM)