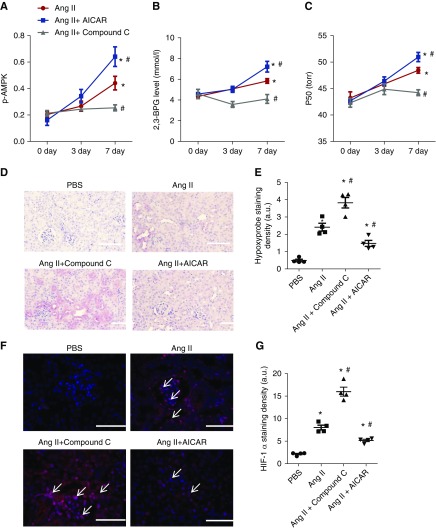
Figure 5.
AMP-activated protein kinase functions downstream of ADORA2B, underlying 2,3-biphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG) production and promoting oxygen delivery to prevent renal hypoxia and disease progression in angiotensin II (Ang II)–induced wild-type (WT) mice. (A–C) AICAR (5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide) treatment significantly stimulated (A) erythrocyte phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK), (B) 2,3-BPG production, and (C) the partial pressure of oxygen to allow 50% of hemoglobin binding to oxygen (P50) levels in Ang II–infused WT mice compared with PBS-treated WT mice in a time-dependent manner, whereas Compound C treatment significantly attenuated (A) erythrocyte p-AMPK, (B) 2,3-BPG production, and (C) P50 levels in Ang II–infused wild-type mice compared with PBS-treated WT mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 for 7 day versus basal level; #P<0.05 for AICAR-treated group versus PBS group and for Compound C–treated group versus PBS group at the same time point (n=5). (D–G) AICAR treatment prevented renal hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression, whereas Compound C treatment aggravated renal hypoxia and HIF-1α expression in WT mice induced by Ang II for 7 days. (D) Immunohistochemical analysis of tissue hypoxia by Hypoxyprobe in kidney. Scale bar, 200 μm. Quantitative image analyses of tissue hypoxia by (E) Hypoxyprobe in kidney and (F) HIF-1α staining in kidneys. Scale bar, 200 μm. *P<0.05 versus PBS-treated WT mice; #P<0.05 versus WT mice with Ang II. (G) Quantitative image analyses of HIF-1α staining in kidney. AICAR- or Compound C–treated WT mice after 7 days of Ang II treatment (n=5). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 versus PBS-treated WT mice; #P<0.05 versus WT mice with Ang II.