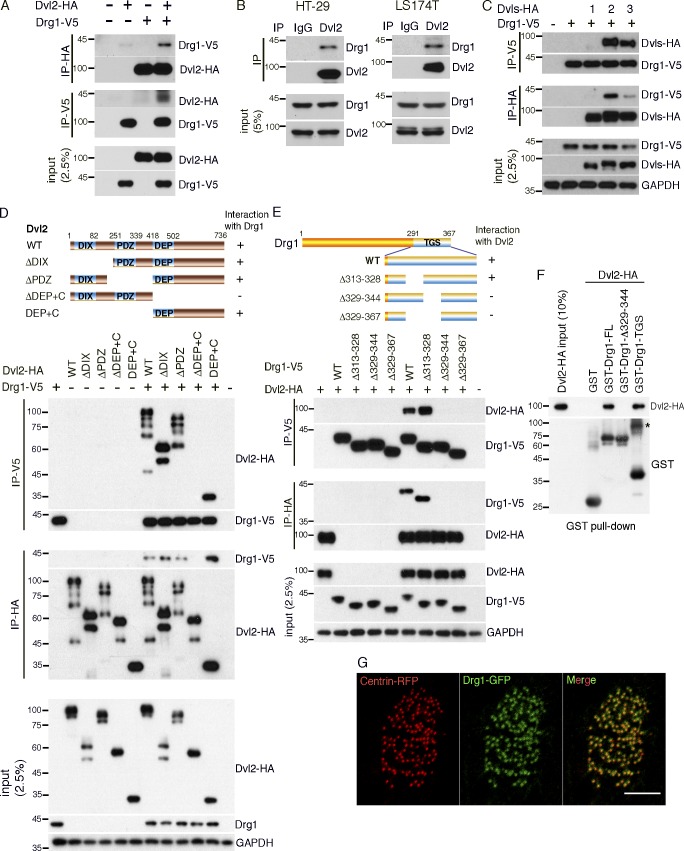
Figure 1.
Drg1 associates with Dvl. (A) Exogenous Drg1 interacts with Dvl2. Dvl2-HA and Drg1-V5 mRNAs were injected in Xenopus embryos, and reciprocal co-IPs were performed. 2.5% of input was loaded. (B) Endogenous Drg1 associates with Dvl2. Using lysates from HT-29 and LS174T colon cancer cells, endogenous co-IPs were performed by precipitating endogenous Dvl2. 2.5% of input was loaded. IgG pull-down is a negative control. (C) Drg1 interacts with Dvl2 and Dvl3, but not Dvl1. The indicated Dvl-HA and Drg1-V5 mRNA were coinjected, and co-IPs were conducted by pull-down in both directions. 2.5% of input was loaded. (D) Drg1 interaction domain mapping of Dvl2. The DEP+C region of Dvl2 is necessary and sufficient to interact with Drg1. The indicated WT and deletion mutants of Dvl2-HA and Drg1-V5 mRNAs were expressed in Xenopus embryos, and co-IPs were performed in both directions. 2.5% of input was loaded. (E) Dvl2 interaction domain mapping of Drg1. WT and the indicated deletion mutants of Drg1-V5 and Dvl2-HA were expressed in Xenopus embryos, and co-IPs were conducted in both directions. Amino acids between 329 and 344 of Drg1 are required for the association with Dvl2. 2.5% of input was loaded. (F) Dvl2-HA associates with Drg1-GST in vitro. 1 µg of the purified recombinant proteins was used for the in vitro binding assay. The asterisk marks a dimerized form of isolated TGS domain. 10% of input was loaded. (G) The subcellular localization of Drg1 in an MCC. Drg1-GFP (green) and centrin-RFP (red, basal body marker) mRNAs were coinjected into the marginal region of both ventral blastomeres at the four-cell stage. The embryos were observed at stage 25. Images were generated by maximum intensity projection from serial z-stack images. Scale bar, 5 µm.