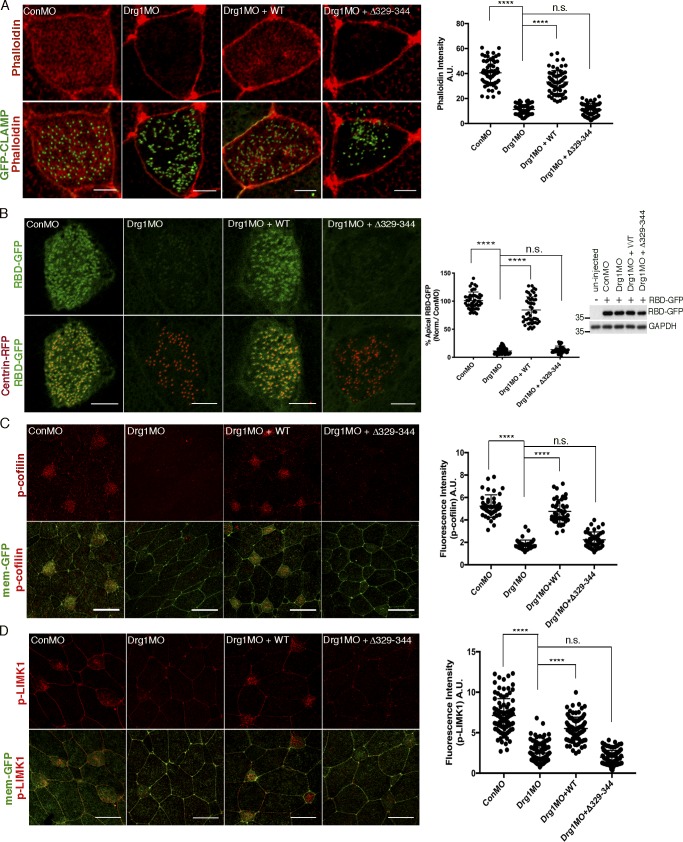
Figure 4.
Drg1–Dvl interaction modulates apical actin enrichment in MCCs through Rho activation. (A) Apical actin meshwork decreases upon Drg1 knockdown. The loss of apical actin signal is rescued by expression of Drg1 WT, but not by the Drg1 Δ329–344 mutant. The embryos were injected with the indicated MOs and mRNAs, fixed at stage 25, and stained with phalloidin (red) to visualize cortical F-actin in apical region of MCCs. GFP-CLAMP (green) marks rootlets. ****, P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA; n = 65. Scale bars, 5 µm. Error bars indicate ± SD. (B) Drg1 knockdown decreases Rho activity. Synthetic mRNAs of RBD-GFP (green) and centrin-RFP (red) were coinjected with the indicated MOs and mRNAs, and embryos were fixed at stage 25. Fluorescence intensity of experimental groups is normalized to the control MCCs and expressed as a percentage relative to control. Expression level of RBD-GFP was tested by Western blot. Images are generated by maximum intensity projection of serial z-stack confocal images from apical (0 µm) to subapical region (−2.5 µm). ****, P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA; n = 49. Scale bars, 5 µm. Error bars indicate ± SD. (C and D) Phosphorylation of Rho downstream targets is decreased by Drg1 knockdown. The embryos injected with the indicated MOs and mRNAs were stained for phospho-cofilin (C) and phospho-LIMK1 (D). Statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Turkey’s multiple range tests. All results are derived from three independent experiments. ****, P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA; n = 42 (C), 40 (D). Error bars represent mean ± SD. Scale bars, 30 µm. a.u., arbitrary units; n.s., not significant.