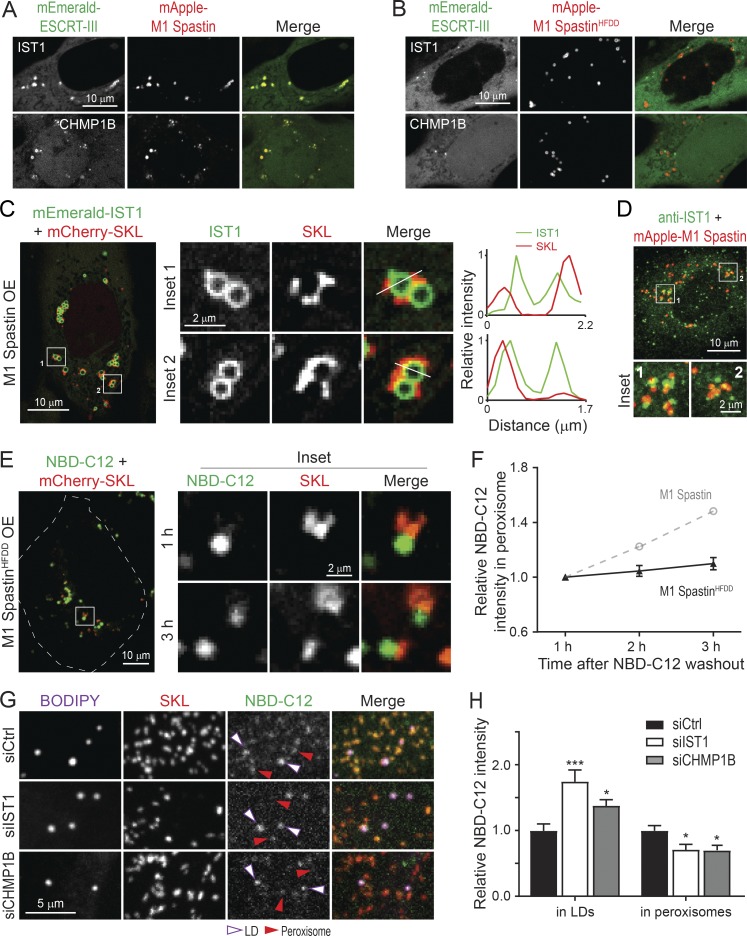
Figure 8.
M1 Spastin recruits IST1 and CHMP1B to LDs to support LD-to-peroxisome FA trafficking. (A and B) Subcellular localization of mEmerald-IST1 (top panels) and mEmerald-CHMP1B (bottom panels) in HeLa cells overexpressing mApple-M1 Spastin (A) or mApple-M1 SpastinHFDD (B). Representative confocal images are shown. (C) mEmerald-IST1 is recruited onto LDs in HeLa cells coexpressing Halo-M1 Spastin, monitored by Airyscan microscopy. Representative images and relative intensity profile are shown. (D) Partial colocalization of immunostained IST1 and mApple-M1 Spastin in HeLa cells. Representative confocal MIP images are shown. (E) Distribution of NBD-C12 in Halo-M1 SpastinHFDD and mCherry-SKL overexpressing HeLa cells following pulse-chase described in Fig. 7 D. Representative confocal images are shown. (F) Relative NBC-C12 intensity in peroxisomes as described in E. Means ± SEM are shown (19 cells from three independent experiments). Gray dashed line is a replica from Fig. 7 F. (G) Distribution of NBD-C12 in BODIPY-665/676–labeled LDs and mCherry-labeled peroxisomes in siCtrl-, siIST1-, or siCHMP1B-treated HeLa cells following NBD-C12 pulse-chase described in Fig. 7 A. Representative confocal MIP images are shown. (H) Relative NBC-C12 intensity in LDs or peroxisomes as described in G. Means ± SEM are shown (25–31 cells from three independent experiments). *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001 compared with siCtrl.