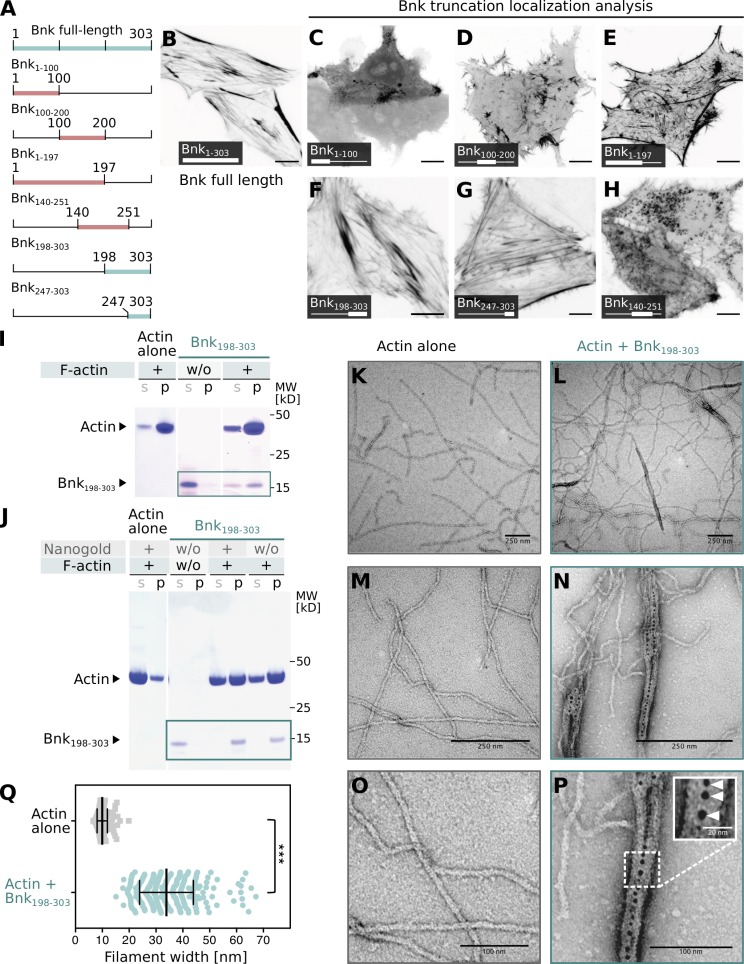
Figure 3.
Bnk protein actin bundling activity localizes to its C-terminal domain. (A–H) Schematic representation of Bnk truncation constructs expressed in mammalian cells (green: localization similar to full-length Bnk; red: mislocalization; A). GFP-tagged Bnk full-length (B) or truncations of GFP-tagged Bnk with Bnk1-100 (C), Bnk100-200 (D), Bnk1-197 (E), Bnk198-303 (F), Bnk247-303 (G), and Bnk140-251 (H) were expressed in HeLa cells and their localization analyzed using confocal microscopy. Bnk198-303 (F) and Bnk247-303 (G) closely resembled the localization of the full-length protein. (I) Coomassie gel of actin-binding assays. While in the absence of actin, purified Bnk198-303 remained in the supernatant fraction (s), in the presence of F-actin, the majority of Bnk198-303 protein copelleted with actin filaments (p). The green box highlights Bnk198-303 protein bands. (J) Coomassie gel of actin-bundling assays. In the presence of F-actin, Bnk198-303 shifted from the supernatant (s) to the pellet fraction (p). The ratio of F-actin in the pellet versus supernatant increased in presence of Bnk198-303. The presence of 5 nm Ni-NTA Nanogold particles did not alter actin or Bnk behavior. The green box highlights Bnk198-303 protein bands. (K–Q) Electron micrographs showing actin fibers alone (K, M, and O) or bound by Bnk198-303 (L, N, and P) at low magnification (K and L), high magnification (M and N), and a further zoom (O and P). Bnk198-303 samples were visualized with gold particles using negative staining. Inset in P shows a zoom of an actin bundle. Arrowheads highlight the localization of Bnk198-303 in the center of the bundle. (Q) Quantification of the width of actin filaments in absence (gray, n = 200) or presence (green, n = 279) of Bnk198-303. Significances were estimated using nonpaired two-sided Student’s t test with ***, P < 0.001.