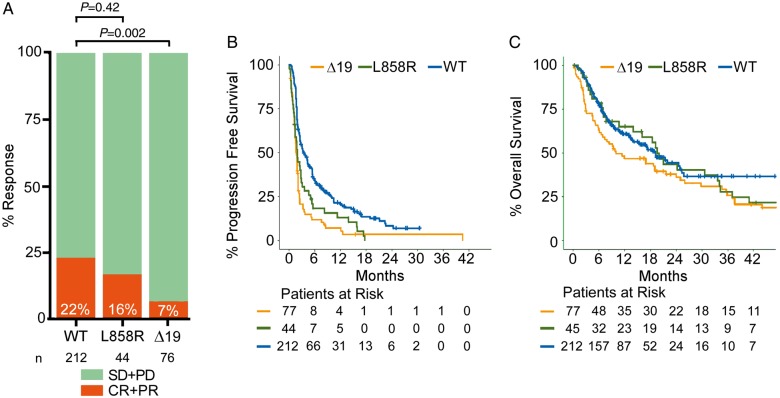
Figure 1.
Response, progression-free survival, and overall survival of EGFRL858Rand EGFRΔ19 mutant tumors to immune checkpoint blockade. (A) Response rate in tumors with EGFRΔ19 (n = 76) or EGFRL858R(n = 44) mutations, and wild-type for EGFR (WT) (n = 212). Overall response rate is indicated on each bar in white. Statistics were calculated using Fisher’s exact test. (B) Progression-free survival in tumors with EGFRΔ19 (n = 77) (HR 0.449, 95% CI 0.338–0.595, log-rank P < 0.001) or EGFRL858R(n = 44) (HR 0.578, 95% CI 0.412–0.811, log-rank P = 0.001) alterations compared with lung tumors that are EGFR wild-type (n = 212). (C) Overall survival in tumors with EGFRΔ19 (n = 77) (HR 0.69, 95% CI 0.493–0.965, log-rank P = 0.03) or EGFRL858R(n = 45) (HR 0.917, 95% CI 0.597–1.409, log-rank P = 0.69) alterations compared with lung tumors that are EGFR wild-type (n = 212). HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.