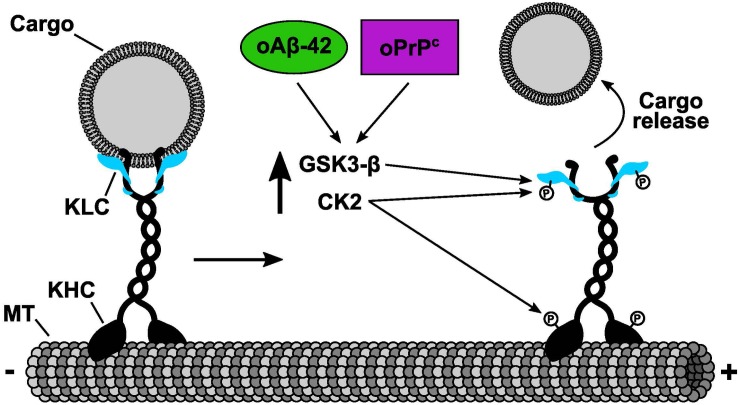
FIGURE 1.
Common molecular mechanism of fast axonal transport inhibition shared by oPrPC and oAβ-42. Cellular and pharmacological data determined that both oPrPC and oAβ-42 induced fast axonal transport inhibition. The inhibitory mechanism was mediated by the activation of endogenous CK2 and GSK3β that in turn phosphorylated KLCs. Phosphorylation of KLCs (letter P on KLCs) promoted the detachment of conventional kinesin from its transported vesicular cargoes. We and others have shown that CK2 can also phosphorylate kinesin-1 heavy chains (KHCs) (letter P on KHCs). Based on our previous results working with KHCs phosphorylation, we predict an additional mechanism of fast axonal transport inhibition induced by CK2 phosphorylation on KHCs which in turn will promote a reduction of kinesin-1 association to microtubules (MTs).