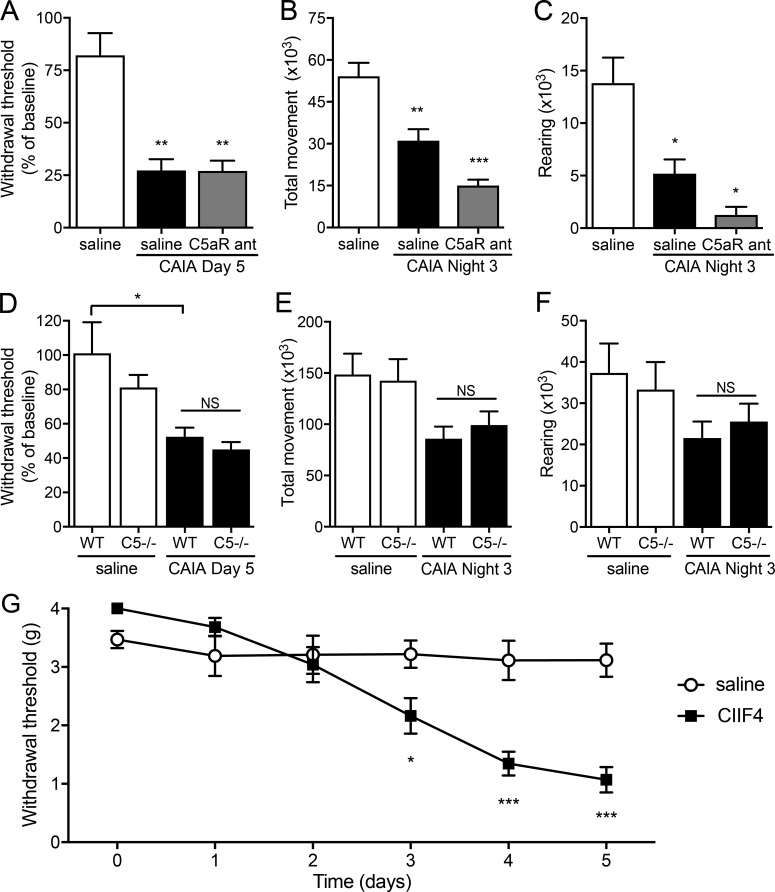
Figure 3.
Anti-CII antibody–induced pain-like behavior is not mediated by complement activation or cartilage destruction. (A) Injection of the C5a-receptor antagonist PMX53 (C5aR ant; n = 5) did not prevent anti-CII mAb–induced mechanical hypersensitivity (n = 4, B10.RIII mice) compared with vehicle (saline)-injected controls (n = 7, B10.RIII mice). (B and C) Antagonizing the C5a-receptor (n = 5, B10.RIII mice) did not prevent anti-CII mAb–induced reduction in total movement (B) and rearing (C) compared with saline controls (n = 19, B10.RIII mice). (D–F) Complement 5–deficient (C5−/−) mice developed mechanical hypersensitivity (D; n = 5) and displayed a reduction in total movement (E) and rearing (F; n = 4) comparable to WT B10Q mice (n = 6–8) after injection of anti-CII mAbs. (G) B10.RIII mice injected with the nonarthritogenic CIIF4 antibody (n = 8) developed mechanical hypersensitivity from day 3 after injection compared with saline controls (n = 7). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 compared with saline controls.