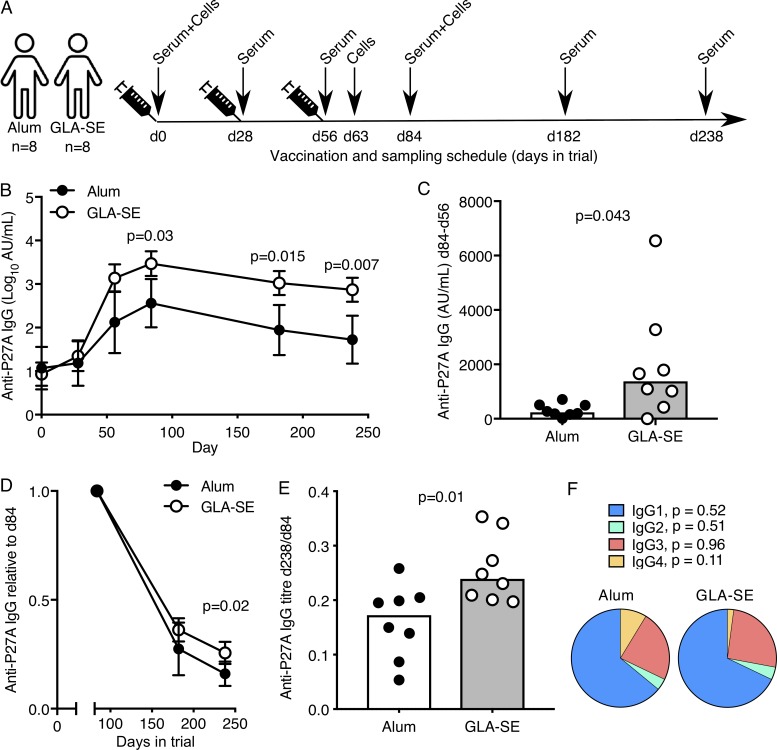
Figure 2.
The adjuvant GLA-SE enhances antibody production but not early ASC expansion. (A) Vaccination and venepuncture schedule for the clinical trial. (B) Anti-P27A IgG antibody titers in volunteers vaccinated with 50 µg P27A peptide in either Alum (black) or GLA-SE (white); error bars represent the 95% confidence interval. Day 0, NS; day 28, NS; day 56, NS; day 84, P = 0.03; day 82, P = 0.015; day 238, P = 0.007. The P values were calculated using a two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple-comparisons test; n = 8/group. Log10 anti-P27A titers are shown. (C) Change in anti-P27A IgG antibody titer 28 d after the third vaccination (d84); n = 8/group; P = 0.043. (D and E) Anti-P27A IgG titer normalized to the peak of the antibody response (d84) in volunteers vaccinated with 50 µg P27A peptide in either Alum (black) or GLA-SE (white); n = 8/group. In D, error bars represent the 95% confidence interval; P = 0.02 (D); P = 0.01 (E). The P values were calculated using a two-way ANOVA. (F) Pie chart of the total anti-P27A IgG pool at day 84 divided by immunoglobulin isotype; n = 8/group. IgG1, P = 0.52; IgG2, P = 0.51; IgG3, P = 0.96; IgG4, P = 0.11. In C and E, the height of the bar represents the median, and each symbol represents one individual; those who received Alum are shown in black, and those who received GLA-SE are in white. In C, E, and F, P values were calculated using a Mann-Whitney U test. Data are from one clinical trial.