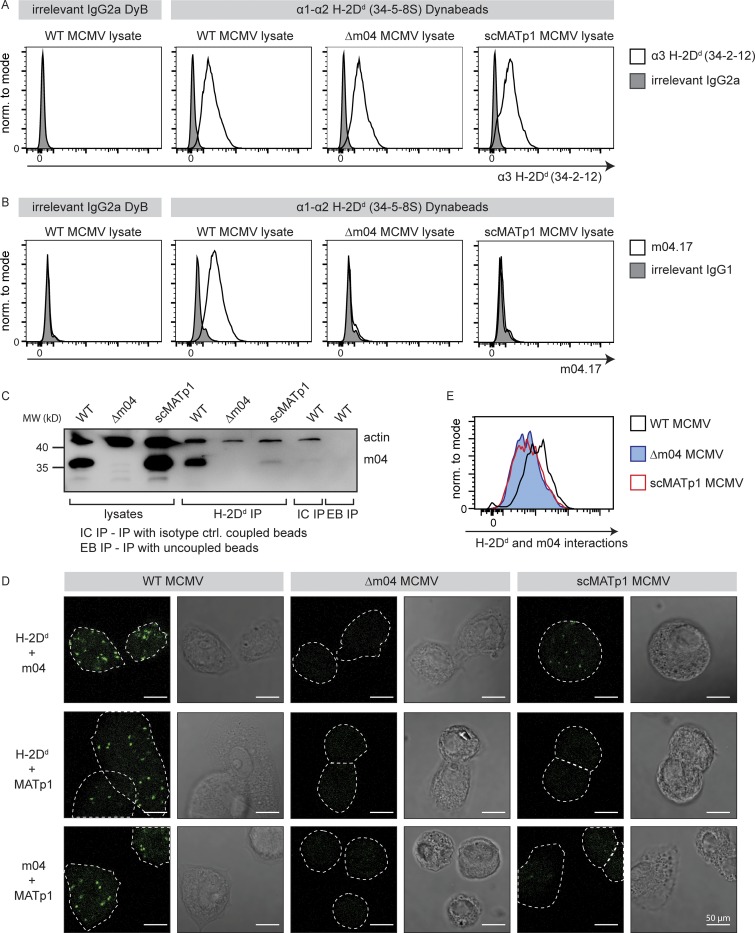
Figure 4.
MATp1 and m04 bind to MHC I molecules cooperatively. (A–C) Coimmunoprecipitation of m04 with MHC I in the presence or absence of MATp1. (A) Epoxy Dynabeads were coupled with 34-5-8S antibody (recognizes α1–α2 domain of H-2Dd molecules) or irrelevant antibody of the same isotype (irrelevant IgG2a DyB). The beads were then incubated for 1 h at 37°C with lysates of BALB/c MEFs infected with WT, Δm04, or scMATp1 MCMV (indicated in the top right corner of histograms). Following incubation, the beads were washed, and an aliquot was stained with 34.2.12-PE antibody (recognizes α3 domain of H-2Dd molecules, indicated on the x axis; A) or with m04.17-biotin antibody (B) followed by streptavidin-PE and detected in flow cytometry. The scheme of the experiment is depicted in Fig. S3 E. (C) Following coimmunoprecipitation described in A, an aliquot of Dynabeads incubated with WT, Δm04, or scMATp1 MCMV–infected cell lysates was washed according to the manufacturer’s protocol, and coprecipitated molecules were eluted and analyzed on 12% SDS-PAGE. m04 was successfully coimmunoprecipitated with H-2Dd only in WT MCMV–infected lysates. m04 was not immunoprecipitated with isotype control antibody coupled (IC IP) or uncoupled (EB IP) beads, indicating that m04 bands eluted from 34-5-8S–coupled beads are coprecipitated m04 and not a consequence of unspecific binding of free m04 from the lysate to the beads. (D and E) PLA (In Situ Duolink for flow and fluorescence; Sigma-Aldrich) demonstrating interactions between m04, MHC I, and MATp1. Primary BALB/c MEFs were infected with 1.5 PFU of indicated viruses and then seeded on glass slides in 12-well plates (D) or seeded on regular cell-culture Petri dishes (E). 24 h p.i., the cells were stained on glass slides (D) or detached using trypsin (E) and then stained with α-MHC I (34-5-8S), α-m04.16, α-MATp1, and secondary antibodies according to the manufacturer’s instructions and described in Materials and methods. In agreement with our coimmunoprecipitation and previous observations (Kleijnen et al., 1997; Lu et al., 2006), m04 and MHC I interacted strongly only in the presence of MATp1 (first row in D and also quantified by FACS in E). MATp1 was shown to interact with both MHC I and m04. There was less interaction between MATp1 and MHC I in virus lacking m04. We thus conclude that MATp1 and m04 interact with MHC I cooperatively. All experiments were performed at least two times. White horizontal bar located at the lower right corner of each image denotes 50 µm. norm., normalized.