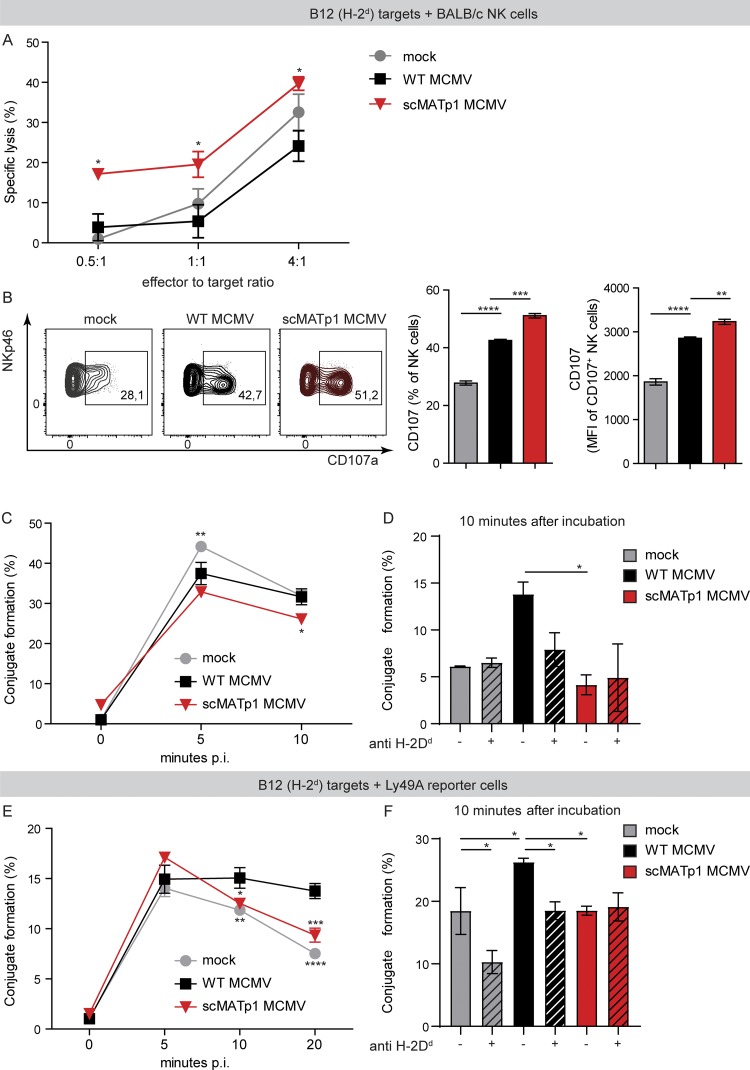
Figure 6.
MATp1 helps infected cells to avoid missing self–dependent killing by NK cells. (A) NK cell in vitro killer assay. Immortalized B12 cells (SV40-transformed BALB/c fibroblasts, targets) were infected with WT or scMATp1 MCMV or left uninfected, labeled with CPD eF670, and after 16 h p.i., cocultured with splenocytes from naive BALB/c mice for another 4 h. Specific lysis of target cells was assessed by staining with PI and measured by flow cytometry. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Data points on the graph represent the mean of a technical triplicate for each sample. (B) Degranulation of NK cells after coincubation with target cells infected with indicated viruses. IL-15–expanded NK cells were cocultured with CPD-labeled and infected targets: B12 cells. Infection and labeling of B12 cells were performed as described in A. Antibody against CD107a was added together with NK cells, and Brefeldin and Monensin after 1 h, followed by another 4 h of incubation. CD107a expression on NK cell population was assessed by flow cytometry. Data are displayed as frequency (%) and mean fluorescence intensity of CD107+ population, and a representative experiment is shown (of three). In each experiment, technical triplicates were analyzed. (C) Conjugate formation between NK and target cells. Target B12 cells were infected and CPD labeled as described in A. IL-15–expanded NK cells were CFSE-labeled and cocultured with CPD+ targets in an E:T ratio of 1:1. After coincubation for indicated times, the reaction was stopped with 1% PFA in PBS, and CDP+CFSE+ doublets were analyzed on a flow cytometer. Graph shows the percentage of infected target cells that are in complex with NK cells. (D) Conjugate formation at 10 min after incubation shown on graph C is dependent on MHC I, as incubation of B12 target cells with α-H-2Dd antibody (34-5-8S) reduced the amount of conjugates by nearly half. (E) Conjugate formation between Ly49A-RCs and target cells. The experiment was performed as described in C, but instead of NK cells, Ly49A-RCs were used as effectors. (F) Conjugate formation between Ly49A-RCs and B12 targets can be prevented by the addition of α-H-2Dd antibody as in D. In C–F, the data are representative of two or three independent experiments where statistical significance of indicated groups compared with WT MCMV–infected samples is shown. One-way ANOVA was used in B, D, and F and two-way ANOVA with post hoc test in A, C, and E. Graphs show mean with SEM as error bars. ****, P ≤ 0.0001; ***, P ≤ 0.001; **, P ≤ 0.01; *, P ≤ 0.05.