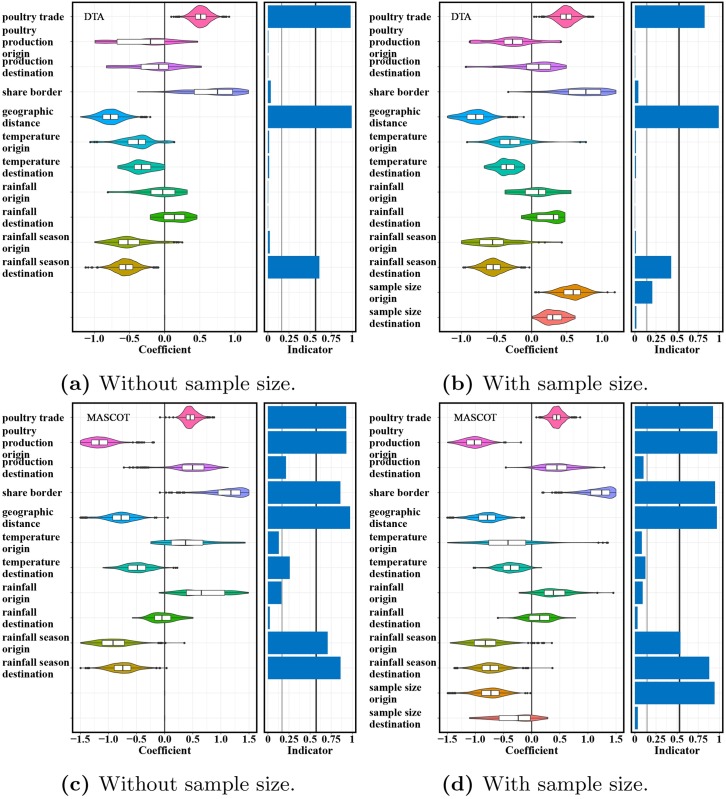
Fig 4. Predictors of migration rates of H9N2 influenza viruses between 12 countries/locations in Asia.
The estimated coefficients and inclusion probabilities for potential predictors of migration rates in the DTA model: (a) without and (b) with isolate sample sizes included as potential predictors; in the time-dependent MASCOT GLMs: (c) without and (d) with isolate sample sizes considered as a predictor. The 50% prior mass was specified on no predictors being included. Coefficients represent the contribution of each predictor to the migration rates of H9N2 AIVs when the corresponding predictor was included in the model. Inclusion probabilities are calculated by proportion of the posterior samples in which each predictor was included in the model. Bayes factor support values of 3 and 20 are represented by a thin and thick vertical line respectively in the inclusion probabilities plot. Geographic distance, poultry trade and rainfall seasonality in destination are the most strongly supported factors to virus spread in Asia under cross-validation in these models. Sample size at origin has an effect, but it doesn’t change the support of other predictors.