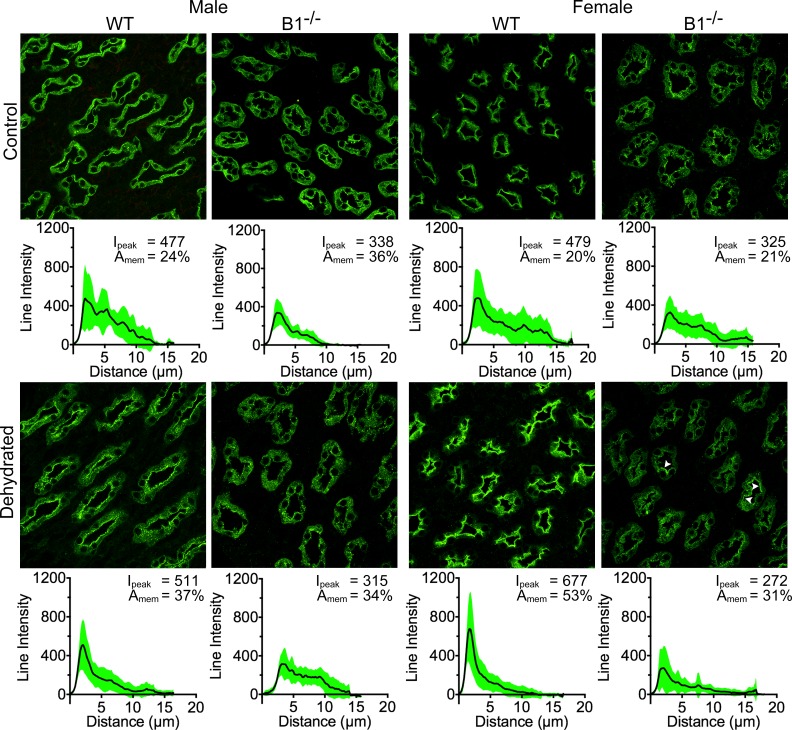
Fig 7. Female WT mice regulate AQP2 more than males in the tip of the inner medulla.
Male WT animals showed little increase of peak intensity after dehydration (only 7%), even though the presence of AQP2 in the membrane region increased by 54% (1st column). On the other hand male B1-/- mice did not exhibit any regulation of AQP2 upon dehydration (2nd column). In contrast, female WT animals had a considerable amount of regulation of AQP2 in this region with a 41% increase in peak intensity and a 160% increase in AQP2 in the membrane region (3rd column). Female B1-/- animals also showed an increase in AQP2 in the membrane vicinity, but peak intensity was reduced (4th column). Similar to the base of IM, there were many cells with a clear membrane expression of AQP2 (white arrowheads) although the overall peak intensity was reduced.