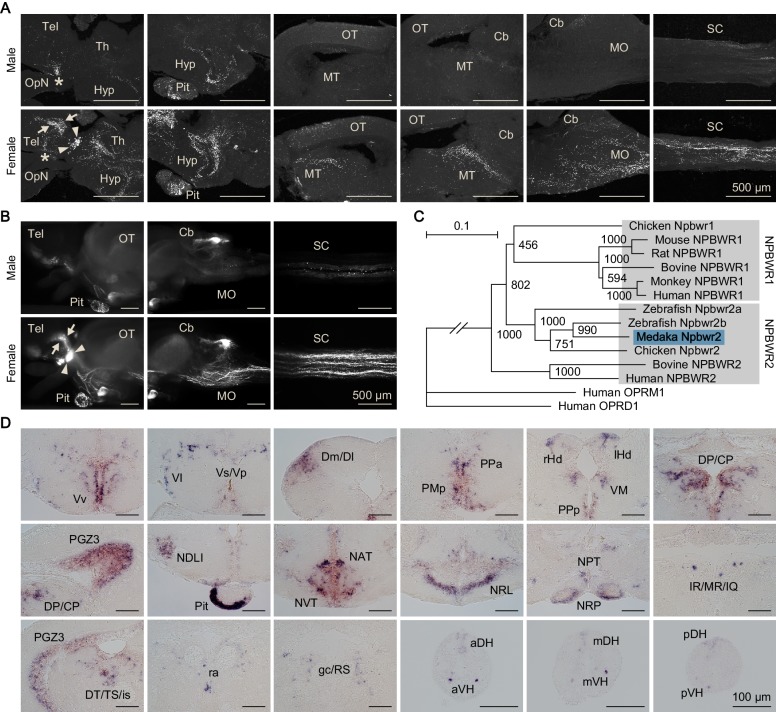
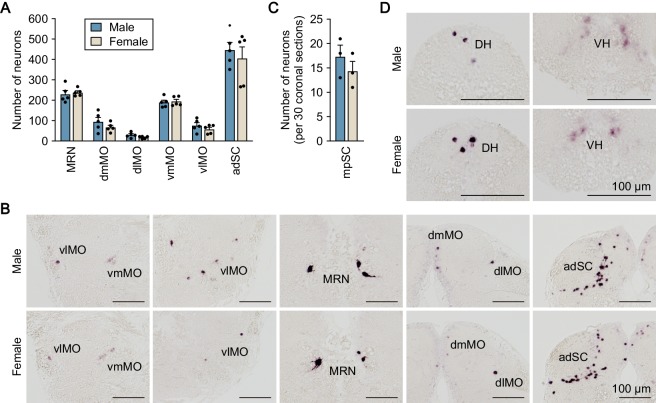
Figure 3. Female-specific Npba likely acts widely in the brain and spinal cord.
(A) Comparison of the distribution of Npba-immunoreactive axons in the brain, pituitary, and spinal cord between males and females. All images are sagittal sections with anterior to the left. Arrows and arrowheads indicate female-specific Npba-immunoreactive neuronal cell bodies in Vs/Vp and PMm/PMg, respectively. Asterisks indicate Npba-immunoreactive neuronal cell bodies in Pbl occurring in both sexes. Scale bars represent 500 μm. For abbreviations of brain regions, see Supplementary file 1. (B) Comparison of the distribution of GFP-labeled axons in the brain, pituitary, and spinal cord between npba-GFP transgenic males and females. Images in the left and middle panels are lateral views with anterior to the left; images in the right panels are horizontal views with anterior to the left. Arrows and arrowheads indicate female-specific GFP-labeled neuronal cell bodies in Vs/Vp and PMm/PMg, respectively. Scale bars represent 500 μm. (C) Phylogenetic tree of NPBWR1 and NPBWR2. The number at each node indicates bootstrap values for 1000 replicates. Human opioid receptors μ1 (OPRM1) and δ1 (OPRD1) were used as the outgroup for tree reconstruction. Scale bar represents 0.1 substitution per site. For species names and GenBank accession numbers, see Supplementary file 3. (D) Distribution of npbwr2 expression in the brain, pituitary, and spinal cord. All images are coronal sections. Images of only males are presented, because there were no obvious sex differences in the distribution of expression (n = 5 per sex). Scale bars represent 100 μm. For abbreviations of brain and spinal cord regions and brain nuclei, see Supplementary file 1. See also Figure 3—figure supplement 1, Figure 3—figure supplement 2, Figure 3—figure supplement 3, and Figure 3—figure supplement 4.
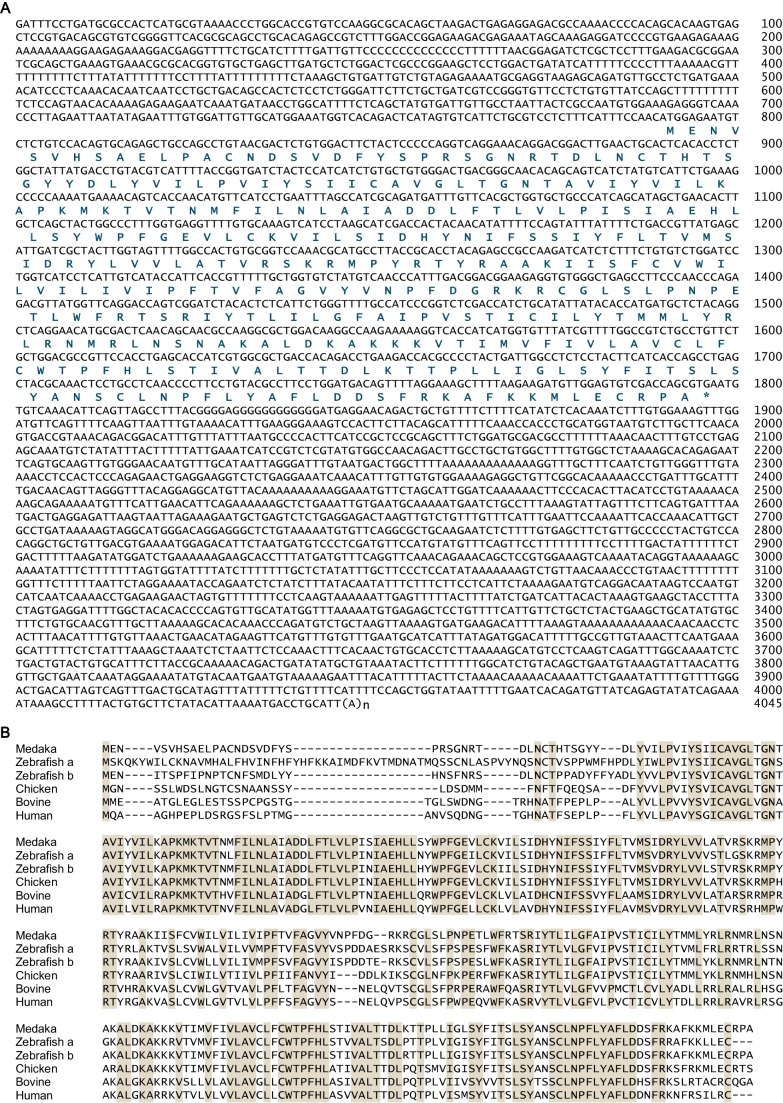
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Verification of the specificity of the anti-Npba antibody.
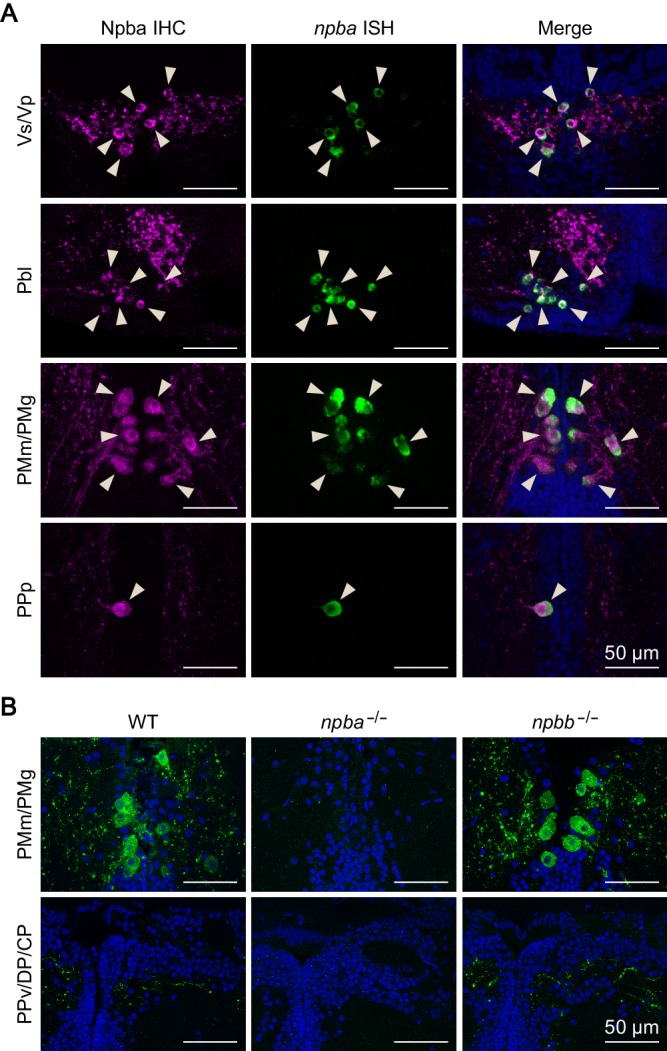
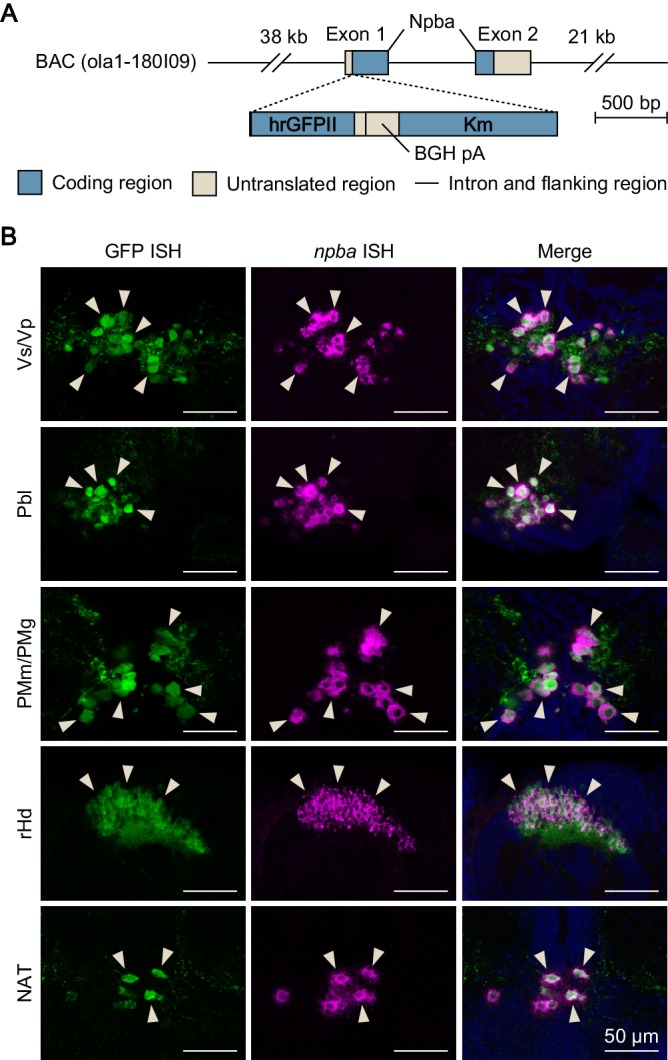
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Generation and verification of npba-GFP transgenic medaka.