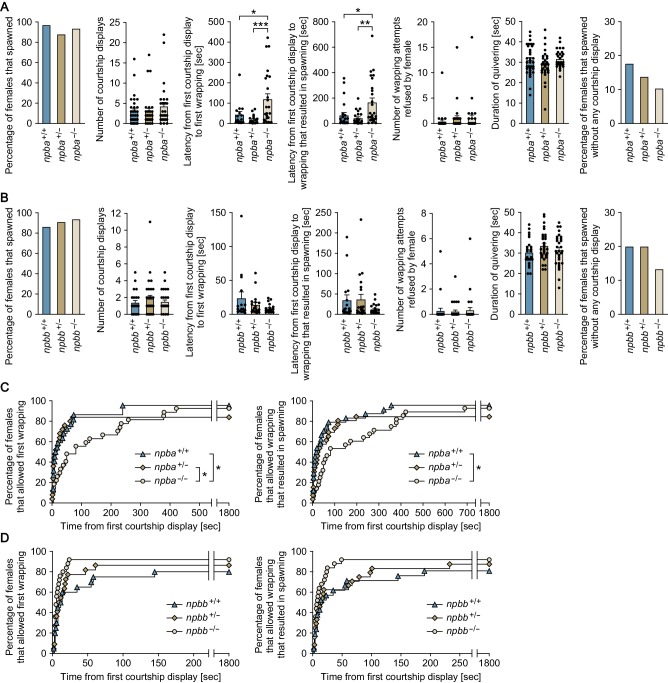
Figure 6. npba is involved in female sexual receptivity.
(A, B) Various parameters in the mating behavior of npba (A) and npbb (B) single knockout females were measured and compared with wild-type females (n = 34, 33, and 31 for npba+/+, npba+/-, and npba-/- females, respectively; n = 29, 33, and 32 for npbb+/+, npbb+/-, and npbb-/- females, respectively). Blue, ocher, and beige columns represent wild-type, heterozygous knockout, and homozygous knockout females, respectively. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001 (Bonferroni’s post hoc test). (C, D) The latency data for npba (C) and npbb (D) single knockouts were further analyzed using Kaplan-Meier plots. Blue triangles, ocher diamonds, and beige circles represent wild-type, heterozygous knockout, and homozygous knockout females, respectively. *, p<0.05 (Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test with Bonferroni’s correction). See also Figure 6—figure supplement 1.