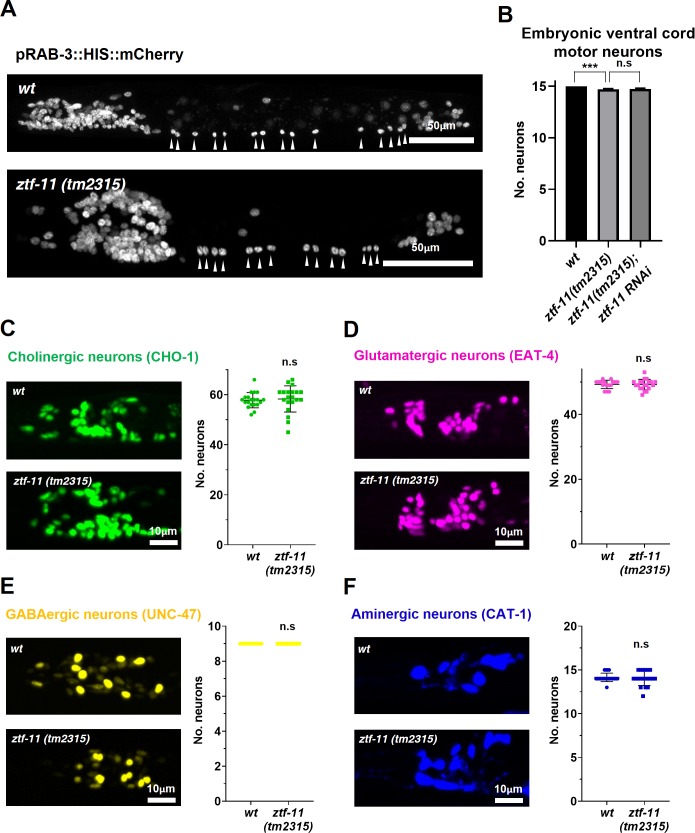
Figure 7. ZTF-11 is mostly dispensable for embryonic neurogenesis.
(A) Pan-neuronal marker expression in wild type and ztf-11(tm2315) L1 larva. Arrowheads point to embryonic ventral cord motor neurons. (B) Number of embryonic ventral cord motor neurons is slightly reduced in ztf-11(tm2315) or ztf-11(tm2315) further treated with feeding RNAi against maternal ZTF-11. Neurons were counted based on pan-neuronal RAB-3 marker expression. Error bars are SD. ****p<0.0001, n.s, p>0.05 Student’s t-test two-tailed, n = 79, 80, 50 animals respectively. See Figure 7—source data 1 for numerical data. (C) ZTF-11 is mostly dispensable for embryonic cholinergic neurons in the head. Left, expression of cholinergic neuron marker, CHO-1, in wild type or ztf-11(tm2315). Right, quantification of counted CHO-1-expressing neurons. (D) ZTF-11 is mostly dispensable for embryonic glutamatergic neurons in the head. Left, expression of glutamatergic neuron marker, EAT-4, in wild type or ztf-11(tm2315). Right, quantification of counted EAT-4-expressing neurons. (E) ZTF-11 is mostly dispensable for embryonic GABAergic neurons in the head. Left, expression of GABAergic neuron marker, UNC-47, in wild type or ztf-11(tm2315). Right, quantification of counted UNC47-expressing neurons. (F) ZTF-11 is mostly dispensable for embryonic aminergic neurons in the head. Left, expression of aminergic neuron marker, CAT-1, in wild type or ztf-11(tm2315). Right, quantification of counted CAT-1-expressing neurons. RIH neuron was very weakly labeled by CAT-1 and only occasionally counted. (C–F) Synchronized early L1 animals by bleaching were used for experiments. Error bars are SD. n.s, p>0.05 Student’s t-test two-tailed, n = 20 animals each. See Figure 7—source data 2 for numerical data.
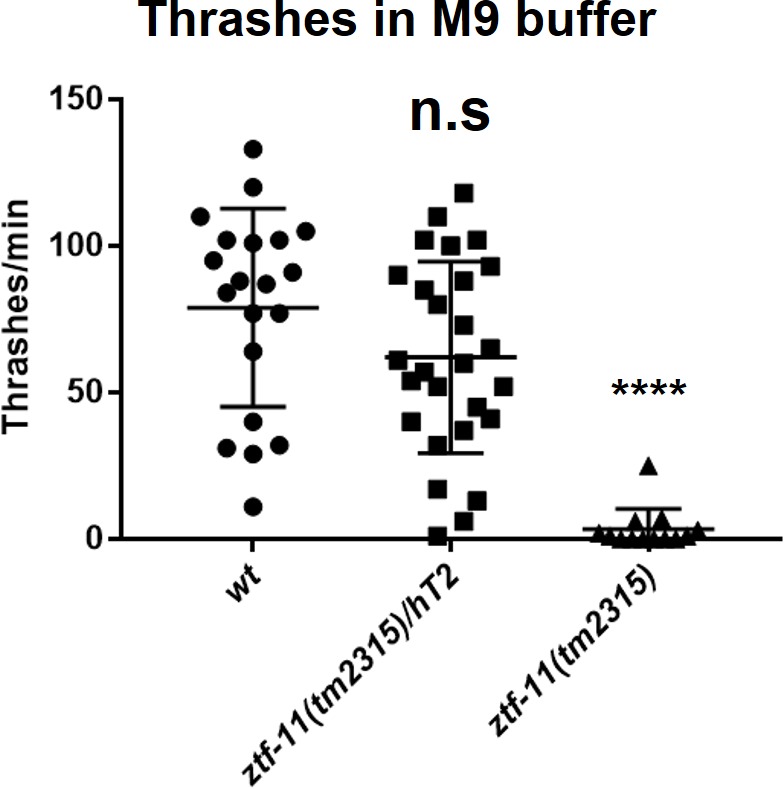
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Embryonic ZTF-11 is required for coordinated motility.