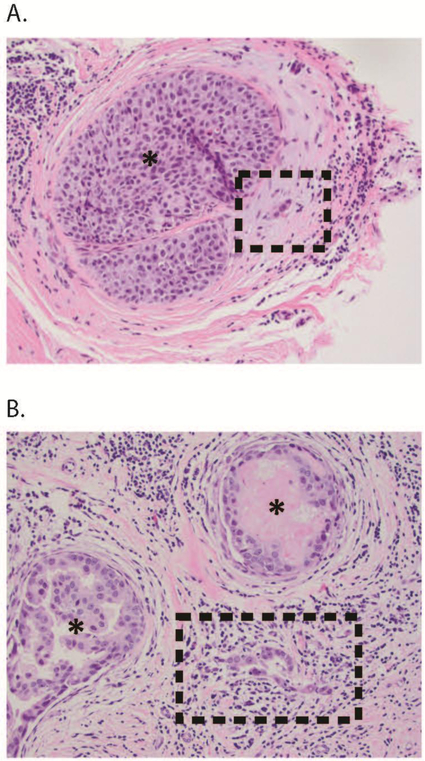
FIG. 1.
(a) Suspected DCISM: here, a cluster of three cells is in the stroma adjacent to a duct containing DCIS (*). Although suspicious, this focus is not definitely diagnostic of microinvasion, and could represent prominent endothelial cells in a small periductal vessel. Work-up with appropriate myoepithelial and/or epithelial markers may help to resolve the differential diagnosis in similar cases. (b) Definite DCISM: here, the microinvasion comprises a cluster of 15–20 neoplastic cells devoid of myoepithelium, spanning <1 mm in the lymphocyte-rich stroma between two ducts (*) harboring DCIS. DCISM ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion, DCIS ductal carcinoma in situ