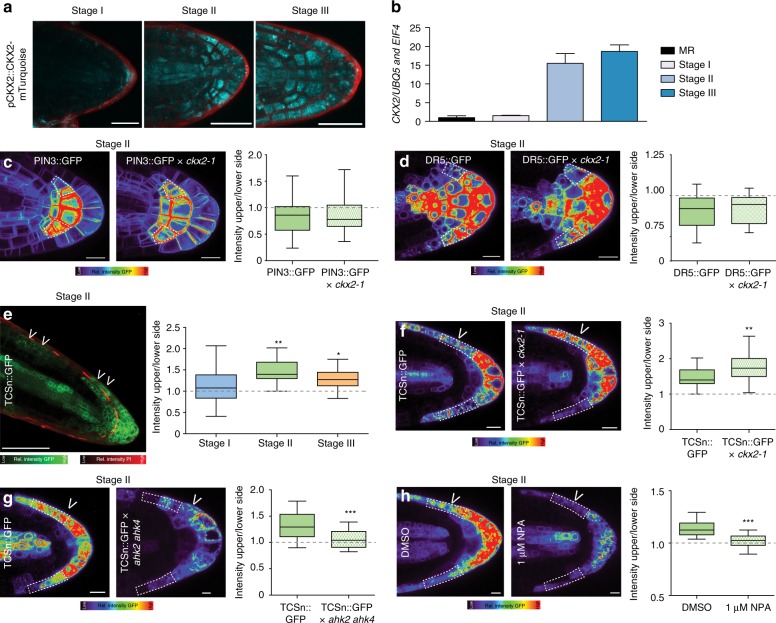
Fig. 6.
CKX2 modulates asymmetric cytokinin signaling in emerged lateral roots. a Representative images of pCKX2::CKX2-mTurquoise in stages I–III LRs. Propidium Iodide (PI) was used for counterstaining. Scale bar, 25 µm. b qPCR analysis detecting the levels of CKX2 transcript in the root tip and LRs stages I–III normalized against UBQ5 and EIF4. Bars represent means ± SD, n = 3. c, d Representative images and signal quantification of stage II LRs of c pPIN3::PIN3-GFP, and d DR5::GFP in Col-0 wild type and ckx2-1 mutant background. Horizontal lines show the medians; box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers extend to the min and max values, n = 10–15 individual LRs. Scale bars, 10 µm. e Representative image (stage II) and quantification of TCSn::GFP in stages I–III LRs. PI was used for counterstaining. Scale bar, 50 µm. f–h Representative images and quantification of stage II LRs of f TCSn::GFP in wild type and ckx2-1, g TCSn::GFP in wild type and ahk2 ahk4 or h after treatment with DMSO or 1 µM NPA for 24 h. Scale bars, 10 µm. e–h One-way ANOVA P-values: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Horizontal lines show the medians; box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers extend to the min and max values, n = 15–30 individual LRs. a–h Experiments were repeated at least three times. White dotted lines outline lateral root cap cells (facing the columella cells) for quantification