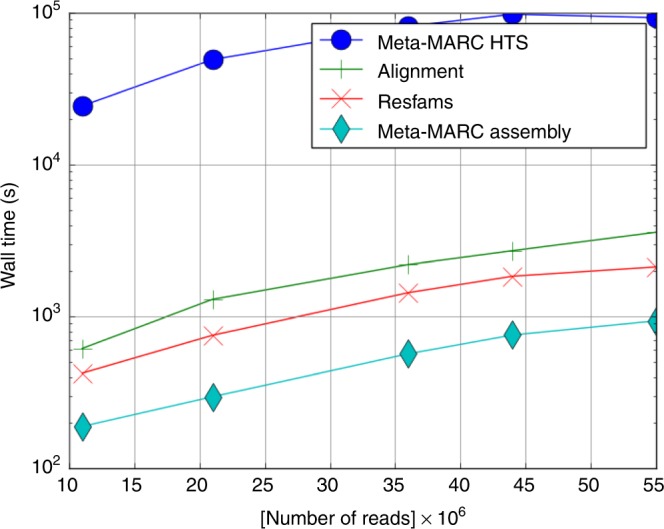
Fig. 7.
Meta-MARC utilizes two workflows to classify and count HTS data: Meta-MARC HTS Reads and Meta-MARC Assembly. Meta-MARC HTS Reads Pipeline: HTS reads are input as FASTQ files to be classified by the HMMER software against the pre-built Meta-MARC Models. Resulting counts are processed to correct for multiple classifications; for example, if a single input read is classified to multiple models, the count for that read is divided evenly between the models to maintain a 1:1 input to output ratio. Meta-MARC Assembly Pipeline: HTS reads are de novo assembled to produce contigs. The HTS reads are then aligned back to these assembled contigs to produce an alignment file. The assembled contigs are annotated by HMMER against the Meta-MARC Models. Using the alignment information, HTS reads that also overlap a Meta-MARC model annotation in the assembled contigs are counted. The resulting counts are processed to correct for multiple classifications as described above. The final output of both pipelines is a corrected count file, listing the number of HTS reads classified to each Meta-MARC Model
