Fig. 2.
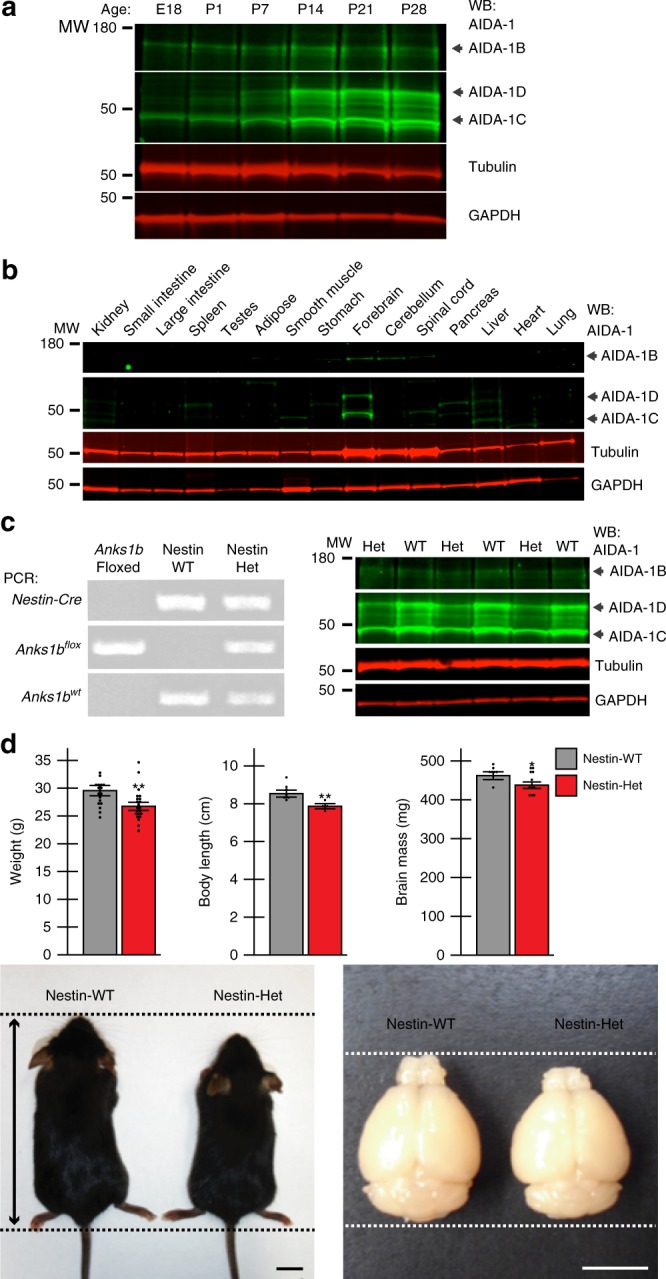
Heterozygous Anks1b knockout mice are viable and show reduced AIDA-1 expression. a Western blots show AIDA-1B is expressed in mouse brain tissue from embryonic development to adulthood. AIDA-1D and 1C expression increases until reaching stable levels in the adult brain. Tubulin and GAPDH levels are shown as loading controls (20 μg lysate). E = embryonic day, P = postnatal day. b AIDA-1 isoforms are selectively expressed in whole mouse brain and cerebellum (20 μg lysate). c (Left) PCR genotyping to identify Nestin-Het mice. (Right) Western blots show reduced expression of AIDA-1 isoforms in Nestin-Het mice (20 μg lysate). d Male Nestin-Het mice show decreased total weight (26.7 ± 0.6 g, mean ± SEM) compared to Nestin-WT controls (29.5 ± 0.8 g); N = 41 mice. Body length was also reduced (7.88 ± 0.09 cm) compared to controls (8.55 ± 0.14 cm); N = 13 mice, scale bar in representative image = 1 cm. Brain mass was also reduced (Nestin-Het = 442.7 ± 8.5 mg, Nestin-WT = 467.5 ± 6.2 mg); N = 19 mice, scale bar in representative image = 0.5 cm. Bar graphs show mean ± SEM, two-sided Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. No statistically significant differences were observed in female mice (Supplementary Data 4)
