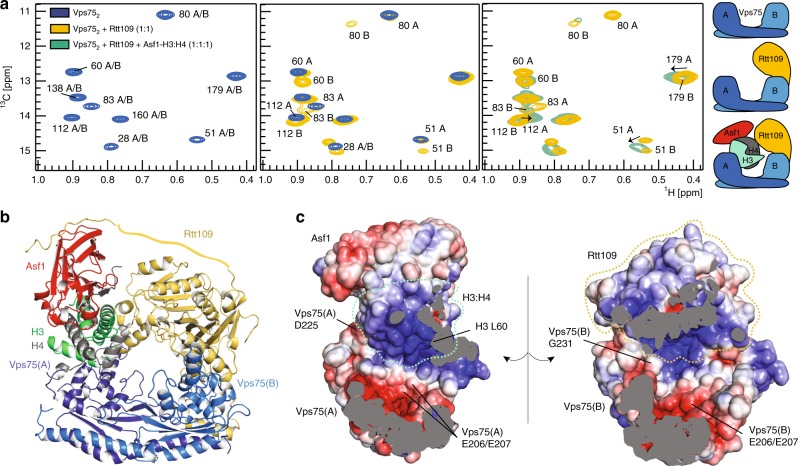
Fig. 1.
Vps752 forms a doughnut-shaped complex with Asf1, H3:H4 and Rtt109. a Overlay of 1H-13C HMQC spectra of ILV methyl-labeled Vps752 in isolation, with Rtt109 and in the Asf1–H3:H4–Rtt109–Vps752 complex. In Vps752, Vps75(A) and Vps75(B) have identical chemical shifts (left). In complex with Rtt109 (middle), only Vps75(B) displays CSPs. Upon further addition of Asf1–H3:H4 (right), the Vps75(B) peaks do not shift further, while Vps75(A) displays noticeable CSPs. Thus, Vps75(B) recruits Rtt109, while Vps75(A) binds Asf1–H3:H4. Spectra were recorded on samples of 60 μM Vps752 in 50 mM sodium citrate pH 6.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM BME at 850 MHz and 298 K. b The Asf1–H3:H4–Rtt109–Vps752 complex adopts a doughnut-like shape with a central cavity of ~25 Å width. The Rtt109 C-terminal tail (Rtt109419–433) is shown bound to Asf1, as described in Lercher et al.34 (PDB entry 6f0y). A flat ribbon indicates the portion of the Rtt109 C-terminal tail for which no structural information is available. The disordered Vps75 and H3 tails are not shown. c Electrostatic surface representation of the inner part of the complex. D225 and G231 are the last structured amino acids of Vps752; L60 is the first amino acid of the H3 core; the Vps75-206EE207 dyad is at the center of an acidic patch