Fig. 6.
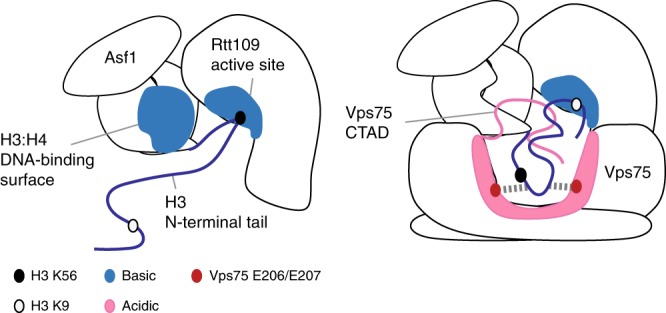
Fuzzy electrostatic interactions promote acetylation of lysine residues in the H3 tail. Left, the mechanism of chaperoning H3-K56 to the Rtt109 catalytic pocket is based on well-known enzyme-recruitment and substrate-presentation processes. Right, the mechanism by which Vps75 chaperones lysine residues in the H3 tail to the Rtt109 catalytic pocket differs from the canonical substrate-presentation process and includes confinement of the H3 tail in the proximity of the Rtt109 catalytic pocket via fuzzy electrostatic interactions occurring between two disordered protein domains, the Vps75 CTAD and the H3 tail.
