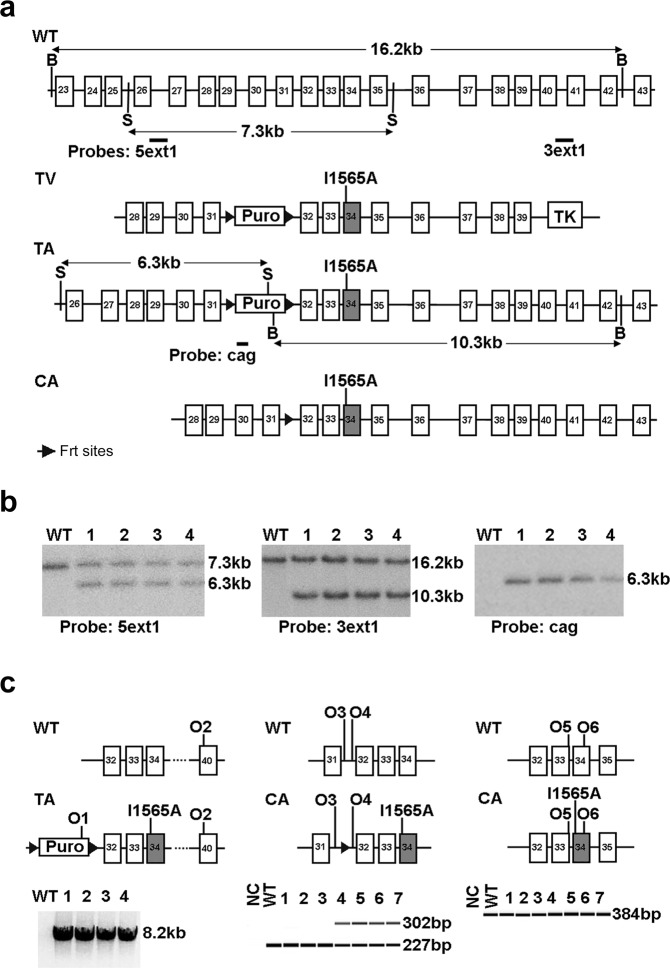
Figure 2.
Knock-in strategy of Igf2r I1565A allele, germ-line targeting and genotyping. (a) Outline of the Igf2r I1565A targeting strategy. Gene exons are shown as boxes (exon 34 shaded), FRT sites as large triangles, WT, wild type; TV, targeting vector; TA, targeted allele; CA, combined allele; Puro, puromycin resistance cassette, TK, thymidine kinase, 5ext1, 3ext1, cag, Southern probes, O1-6, oligos 1–6 (b) To detect correct homologous recombination at the 5′ end of the construct, 5 clones of ES cells were digested with PspOMI and hybridised to probe 5ext1 (left panel), 4 clones gave the expected band at 6.3 kb. For the 3′ end of the construct, cells were digested with NsiI and hybridised to probe 3ext1 (central panel), all 4 gave the expected band at 10.3 kb. To detect a single insertion site, clones were digested with NsiI and hybridised to probe cag, and all 4 gave a single band at the correct size of 6.3 kb (right panel). (c) Genotyping PCR analysis on pups bred from clone 2 in (b) (Left panel); 8.2 kb fragment of TA amplified by oligos 1 and 2 denotes the presence of full complement of exons downstream of I1565A. (Middle panel; following cross with Flp deleter to generate CA); 302 bp fragment amplified by oligos 3 and 4 denotes the presence of the I1565A knock-in allele, and is the basis for genotyping. (Right panel; following cross with Flp deleter to generate CA); 384 bp fragment amplified by oligos 5 and 6 denotes identical product size for both wild-type I1565A knock-in allele.