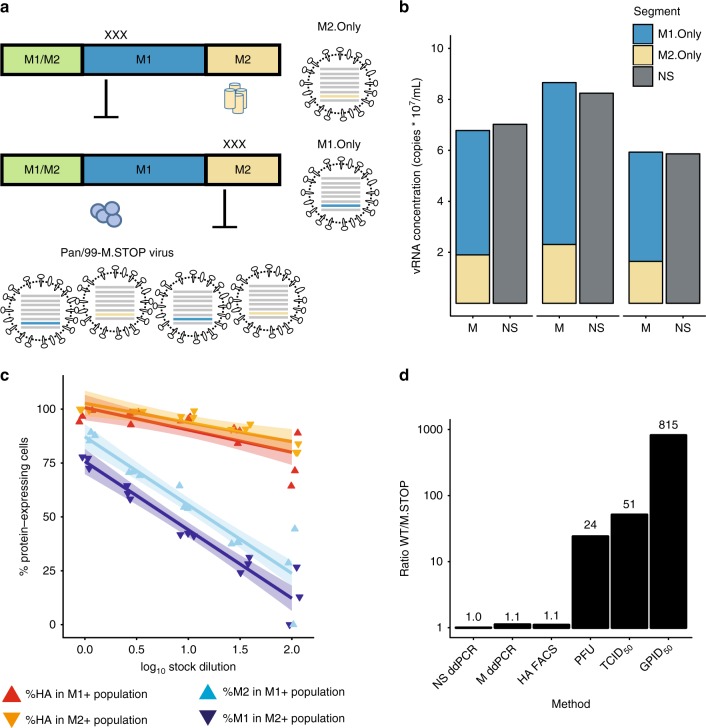
Fig. 7.
Dependence on complementation hinders viral infectivity. a Mutation scheme used to generate M1.Only and M2.Only segments, and Pan/99-M.STOP virus. b Copies of M1.Only, M2.Only, and NS segments in three separate aliquots of Pan/99-M.STOP virus stock were quantified by digital droplet PCR. c Cells were inoculated with Pan/99-M.STOP virus, and incubated under single-cycle conditions before staining for HA, M1, and M2 expression (N = 3 replicates per dilution). The percentage of cells expressing M1, M2, and HA within M1+ or M2+ subpopulations is shown at each dilution. Lines represent linear regression with shading representing 95% CI (mean ± 1.96 * SE). d Titers of WT and M.STOP virus stocks were quantified by ddPCR targeting the NS segment (N = 2 (WT) or 3 (M.STOP) replicates), ddPCR targeting (any) M segment (N = 2 (WT) or 3 (M.STOP) replicates), immunotitration by flow cytometry (N = 1 replicate per virus per dilution), plaque assay (N = 6 replicates per virus), tissue culture ID50 (N = 4 replicates per virus per dilution), and guinea pig ID50 (N = 4 animals per virus per dose). All results are normalized to the ratio of NS ddPCR copy numbers. Source data are provided as a Source Data file