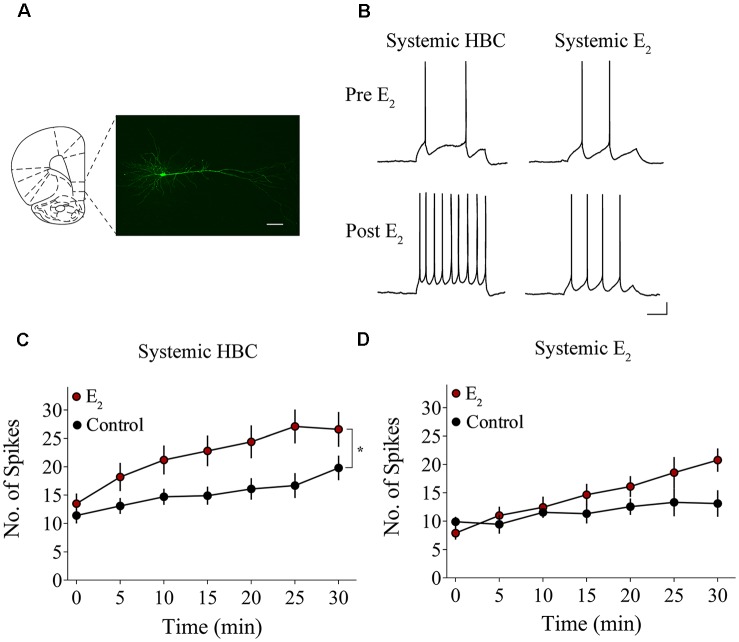
Figure 2.
Bath-application of E2 potentiates IL-mPFC pyramidal neuron excitability. (A) Photomicrograph of a biocytin-filled IL-mPFC pyramidal neuron. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) Individual traces of current-evoked action potentials (APs) from IL-mPFC pyramidal neurons before (top) and after (bottom) bath-application of E2 in slices from ovariectomized (OVX) female rats that were systemically injected with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HBC)-vehicle (left) or with E2 (right). Scale bars, 10 mV (vertical) and 500 ms (horizontal). (C) Compared to artificial cerebral spinal fluid (aCSF) alone (n = 10), bath-application of E2 (n = 10) enhances intrinsic excitability in IL-mPFC neurons from OVX female rats that were systemically injected with HBC-vehicle prior to recordings. (D) Compared to aCSF alone (n = 9), bath-application of E2 (n = 9) does not enhance intrinsic excitability in IL-mPFC neurons from OVX female rats that were systemically injected with E2 prior to recordings. *p < 0.05. Error bars indicate SEM.