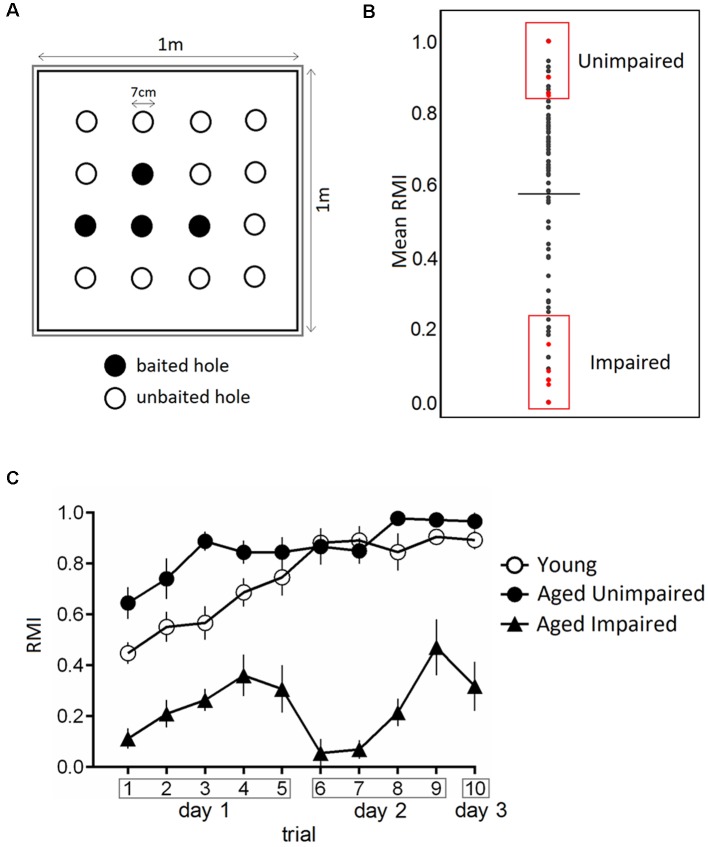
Figure 1.
Performance in the hole-board test. (A) Schematic of the hole-board maze, a non-sophisticated paradigm for the evaluation of spatial memory. Animals have to learn and remember position of four baited holes during 3 days in 10 trials. (B) From a large cohort of 160 male Sprague–Dawley rats, 22–24 months old, impaired and unimpaired performers were selected based on their mean Reference Memory Index (RMI) derived from trial 6 and 10 ± 1 standard deviation (SD). The dashed line indicates the mean of mean RMIs. (C) Performance of young, aged impaired (AI) and aged unimpaired (AU) rats in the hole-board test. The data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 9. AU animals performed the task comparable to young rats.