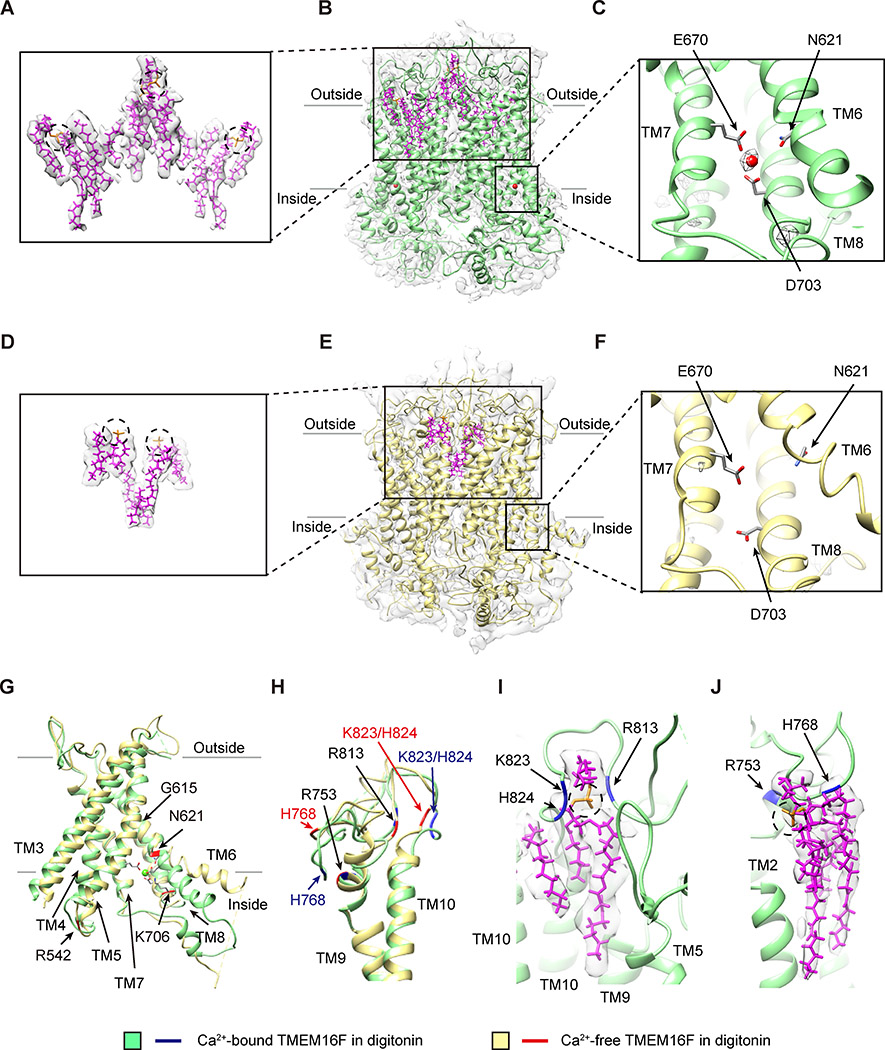
Figure 1. Ca2+-Dependent Conformation Changes and Lipid Binding to TMEM16F.
(A–C) Lipids with slanted orientations (model in magenta, superimposed on the sharpened density map in light gray; A) are associated with Ca2+-bound TMEM16F in digitonin (green) with lipids (magenta) and one Ca2+ ion (red sphere) in each monomer, overlaid on the electron density map (sharpened, in light gray; B). The Ca2+ ion is coordinated by N621 on TM6, E670 on TM7, and D703 on TM8 (C).
(D–F) Fewer lipids (model in magenta, superimposed on the sharpened electron density map in light gray; D) are associated with Ca2+-free TMEM16F in digitonin (yellow) with lipids (magenta) overlaid on the electron density map (sharpened, in light gray; E). TM6 remains close to TM7 and TM8 even without Ca2+ binding to the acidic residues on these transmembrane helices (F).
(G) Superimposition of ribbon diagrams of Ca2+-bound (green) and Ca2+-free (yellow) TMEM16F in digitonin, showing a bend of TM6 at G615 in Ca2+-bound, but not Ca2+-free, TMEM16F and R542, N621, and K706 with Ca2+-dependent placements.
(H) Superimposition of ribbon diagrams of Ca2+-bound (green) and Ca2+-free (yellow) TMEM16F in digitonin, showing different conformations of TM9-TM10 loop.
(I) A lipid with its headgroup coordinated by R813, K823, and H824 on TM9-TM10 loop of Ca2+-bound TMEM16F in digitonin (green).
(J) A lipid with its headgroup coordinated by R753 and H768 on TM9-TM10 loop of Ca2+-bound TMEM16F in digitonin (green).
See also Figures S1 and S2 and Table S1.