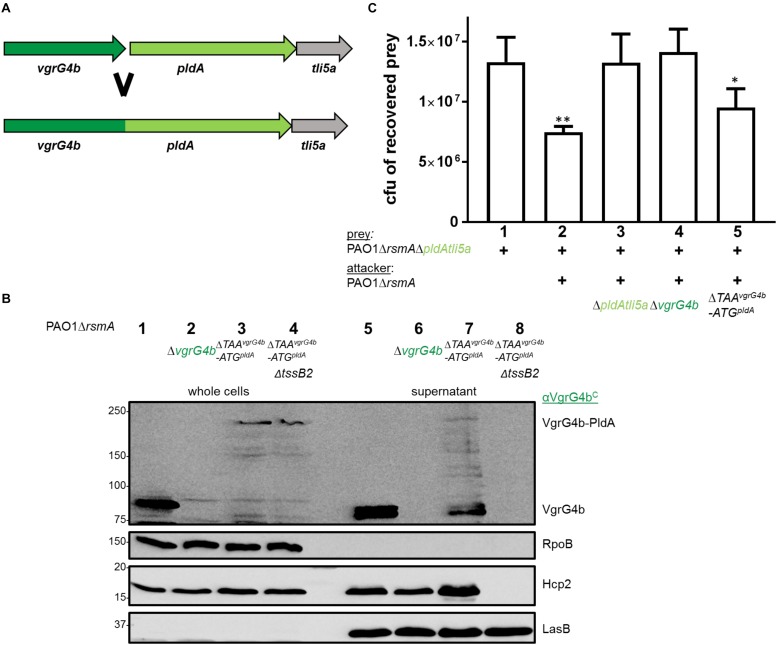
FIGURE 9.
VgrG4b can deliver PldA when fused to its C-terminus. (A) The STOP codon of vgrG4b, the intergenic region and START-codon of pldA were deleted resulting in a single chimeric gene product. (B) Representative figure of a western blot from a secretion assay using PAO1ΔrsmA with an active or inactive H2-T6SS (ΔtssB2) encoding VgrG4b-PldA (ΔTAAvgrG4b-ATGpldA). As a positive control for VgrG4b secretion, PAO1ΔrsmA (lane 1) was included, while the negative control lacked vgrG4b (lane 2). Antibodies used (from top to bottom) are against VgrG4bC, RpoB, Hcp2 and LasB, a T2SS substrate (Olson and Ohman, 1992) acting as a loading control for the supernatant, as indicated on the right. (C) Bacterial competition represented by plots of recovered cfu of prey strain PAO1ΔrsmAΔpldAtli5a:: lacZ after contact with the attacker strain encoding WT PldA, WT VgrG4b or the fusion VgrG4b-PldA (ΔTAAvgrG4b-ATGpldA) as indicated. As a positive control for PldA-mediated killing, PAO1ΔrsmA was included (lane 2) while the negative controls lacked pldAtli5a (lane 3) or vgrG4b (lane 4). Spots were incubated for 24 h at 25 ∘C in a 1:1 ratio. One-Way ANOVA analysis with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test was conducted on the data set obtained from the recovered prey on its own with ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01.