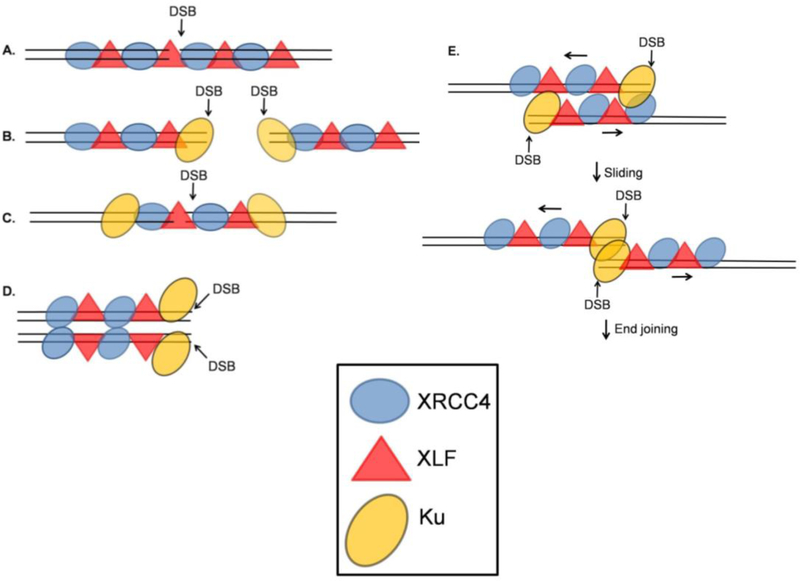
Figure 3.
Different possible arrangements of XRCC4/XLF filaments with respect to DSBs. A. An XRCC4/XLF filament spans a DSB, aligning the DNA ends on either side of the break. This model does not clearly explain how DNA-PKcs and other processing enzymes gain access to the DNA DSB. B. XRCC4/XLF filaments form adjacent to terminally bound Ku. C. An XRCC4/XLF filament spans a DSB after translocation of Ku away from the DSB end. D. XRCC4/XLF filaments aligned side-by-side position two DNA molecules such that processing and ligation can occur at the exposed DSB ends. E. XRCC4/XLF filaments, each binding a DNA segment near a DSB, align side-by-side, then slide to bring the DSB ends into juxtaposition. Adapted from [45, 46, 47].