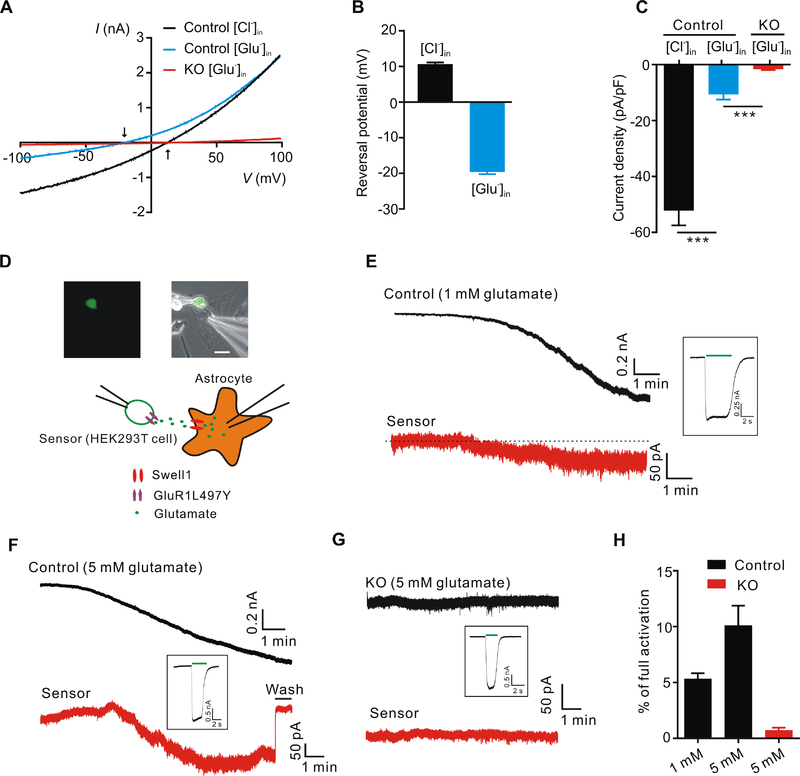
Figure 2. Swell1-dependent VRAC is a glutamate-releasing channel.
(A) Representative whole-cell currents recorded by ramp protocol from −100 to +100 mV in HYPO solution from control and Swell1 KO astrocytes with Cl−-based (133 mM CsCl) or glutamate-based (133 mM Cs-glutamate) pipette solution. Arrows indicate the reversal potentials.
(B) Quantification of the reversal potentials of control astrocytes. n = 11 cells for each group.
(C) Quantification of current densities at −100 mV evoked by HYPO from control and Swell1 KO astrocytes with Cl−-based or glutamate-based pipette solution. n = 9 cells for each group. Student’s t tests, *** p < 0.001.
(D) Representative images (top) and schematic illustration (below) of sniffer-patch technique. The small GFP positive cell is the HEK293T sensor cell expressing GluR1-L497Y. Astrocyte is whole-cell patched with hypertonic pipette solution (400 mOsm/kg, containing 1 or 5 mM glutamate). Scale bar, 20 μm.
(E-G) Representative current traces recorded at holding potential of −60 mV from control astrocytes (E and F), Swell1 KO astrocytes (G) and the sensor cells (red). The inward currents in the astrocytes indicate VRAC activation. The inward currents in the sensor cells indicate the detection of glutamate release from the nearby astrocytes. After the experiment, full current activation in the sensor cells (inset) was recorded by bath application of 5 mM glutamate (green line).
(H) Quantification of the percentage of full activation in control (n = 8 cells) and Swell1 KO astrocytes (n = 6 cells).
Data are reported as mean ± SEM. Cultured astrocytes were independently isolated from 2 mice for each genotype.