Table 3. Comparing properties of isomers 2, 22, and 23via DFT calculations a .
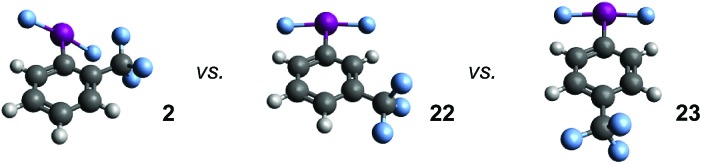
| ||||||||
| Subs. | d(C–I) | d(I–F) | q C | q I | q F | θ C–I–F | θ F–I–F | φ C–C–I–F b |
| o-CF3 | 2.13 Å | 2.01 Å c | –0.248 | 1.419 | –0.627 d | 86° e | 172° | 40° f |
| m-CF3 | 2.13 Å | 2.02 Å g | –0.251 | 1.409 | –0.628 | 87° | 174° | 0° |
| p-CF3 | 2.13 Å | 2.03 Å h | –0.300 | 1.502 | –0.649 | 87° | 175° | 0° |
aCalculations peformed at wB97xD/cc-pvdz, with a cc-pvdz-PP basis set used for the iodine atom. C refers to ipso carbon atom and F refers to fluorine atom bound to iodine, unless otherwise specified.
bDihedral angle of Cortho–Cipso–I–F.
cAverage between 2.00 and 2.02 (not equal bond lengths).
dAverage between –0.621 and –0.633.
eAverage between 85° and 87°.
fF atom proximal to substituent (dihedral angle is 38° for distal F).
gStructure is nearly symmetric about F–I–F (mirror plane).
hStructure is symmetric about F–I–F (mirror plane).
