Table 1. Mechanistic Study and Optimization of the Ar–Cl Cross-Ullman Reaction.
| entry | change from the optimized conditionsc | 3a (%)d |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | none | 84 |
| 2 | NaCl instead of LiCl | 62 |
| 3 | LiBr instead of LiCl | 59 |
| 4 | Bu4NCl instead of LiCl | 53 |
| 5 | TMSCl instead of LiCl | 16 |
| 6 | no LiCl | <10 |
| 7 | Mn instead of Zn | 62 |
| 8 | Mn instead of Zn, LiBr instead of LiCl | 77 |
| 9 | without PdCl2 and dppb | 44 |
| 10 | without NiCl2(dme) and dtbbpy | <5 |
| 11 | reaction set up on the benchtope | 80 |
| 12 | 1.2 equiv of 2a | 90 (89f) |
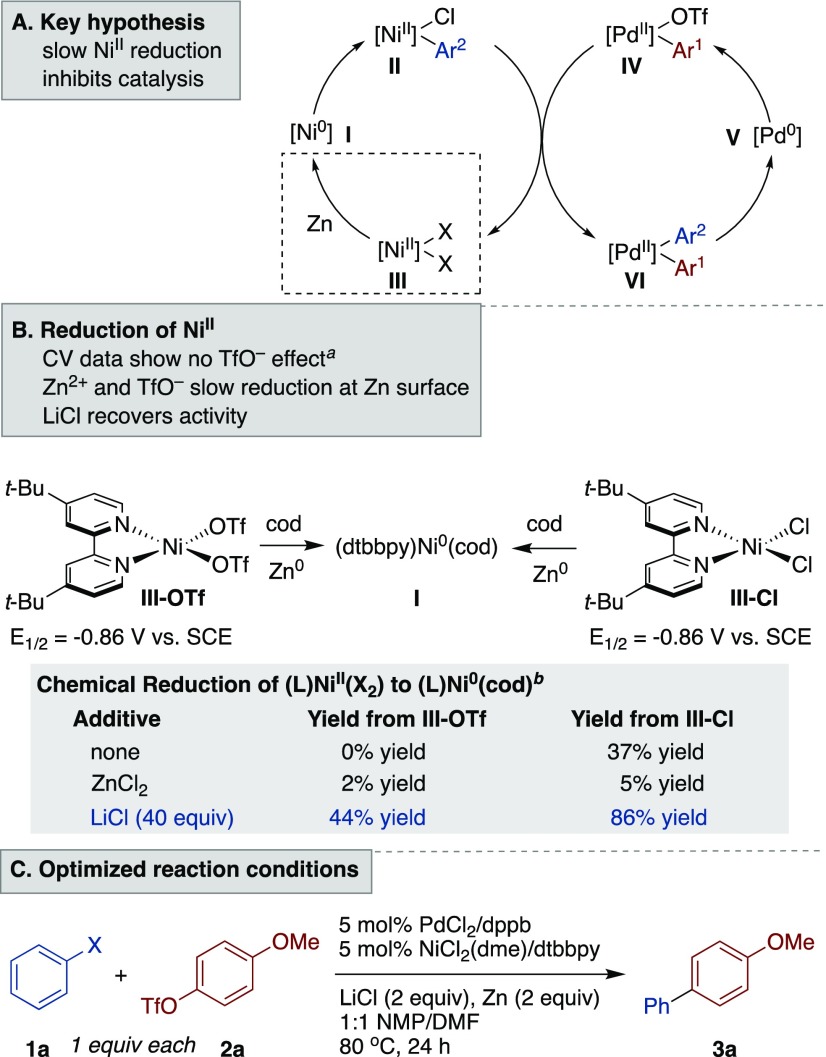
In DMF. See the Supporting Information for details on electrochemical studies.
Reduction of III was conducted in DMF at a concentration of 0.025 M with Zn powder (40 equiv). Cyclooctadiene (0.125 M) was added to stabilize the product. Salts (1–40 equiv) were added in some cases. See the Supporting Information for additional results and experimental details.
Reactions were run on a 0.5 mmol scale in 2 mL of solvent. NMP = N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone.
GC yield vs dodecane as an internal standard.
The reaction was set up under air with dry solvent.
Isolated yield.