Scheme 1. NAD+ Biosynthesis Pathways.
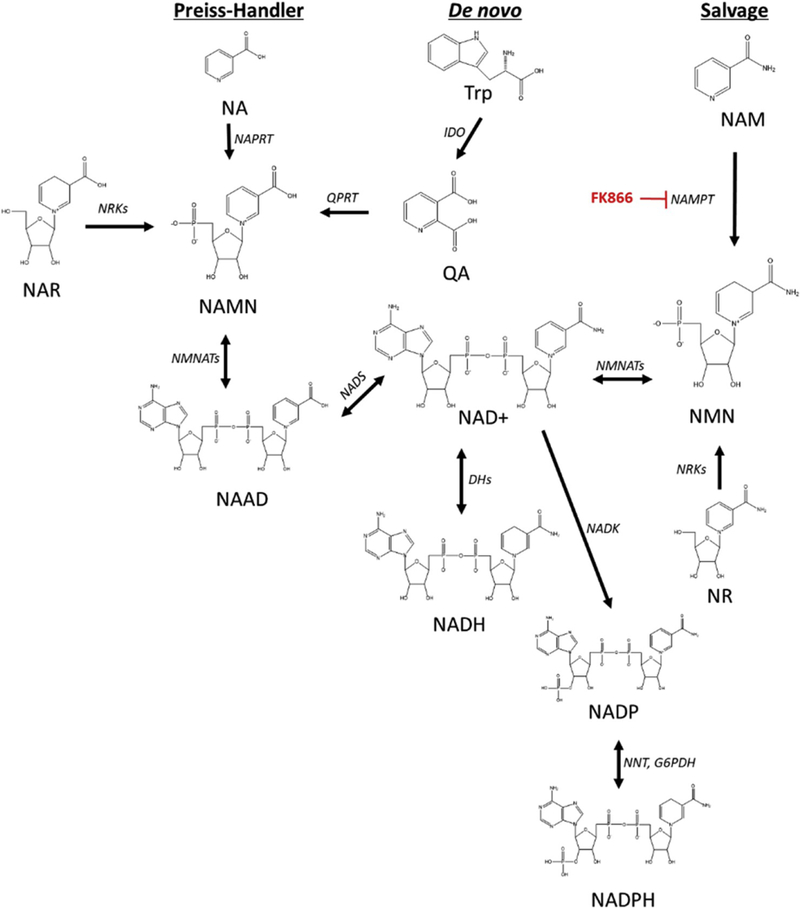
Three main pathways of NAD+ metabolite biosynthesis are the Preiss-Handler, de novo, and salvage pathways [6,7]. Chemical structures and synthesis enzymes (italics) for each metabolite are depicted. Nicotinic acid (NA), Quinolinic acid (QA), NA mononucleotide (NAMN), NA adenine dinucleotide (NAAD), NA riboside (NAR), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), NAD+, reduced (NADH), NADphosphate, oxidized (NADP), NADphosphate, reduced (NADPH), nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), nicotinamide (NAM). Quinolinate phosphoribosyl transferase (QPRT), nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase (NAPRT), nicotinamide riboside kinases (NRKs), Dehydrogenases (DHs), nicotinamide mononucleotide adenyl-transferases 1–3 (NMNATs), NADsynthetase (NADS), Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), NADkinase (NADK), Nicotinamid riboside (NR), nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (NAMPT), NAD(P) transhydrogenase (NNT), FK866 is a NAMPT inhibitor.
