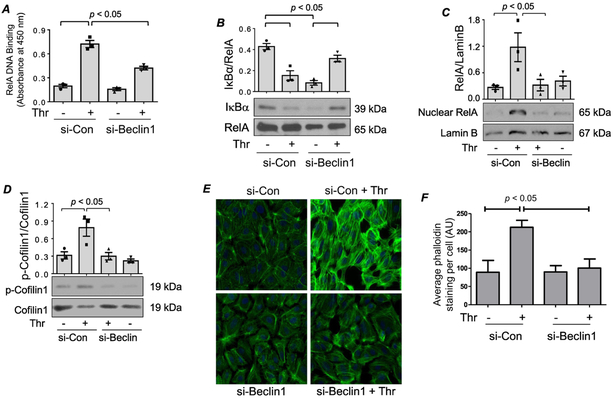
Figure 3. (A-B) Knockdown of Beclin1 inhibits RelA/p65 nuclear DNA binding without affecting IκBα degradation.
HPAEC were transfected with si-Con or si-Beclin1 48 h prior to treatment with thrombin for 1 h. (A) An ELISA-based assay was used to assess RelA/p65 DNA binding activity as described in the Materials and Methods. Bars indicate mean ± SEM (n = 3) for each condition, and were analyzed by ANOVA. (B) Total cell lysates were prepared and Western blots were performed to determine IκBα and RelA/p65 levels. Bars indicate mean ± SEM (n = 3) for each condition, and were analyzed by ANOVA. (C-F) Knockdown of Beclin1 prevents RelA/p65 nuclear translocation via inhibition of cofilin1 phosphorylation and actin stress fiber formation. HPAEC were transfected with si-Con or si-Beclin1 48 h prior to treatment with thrombin for 1 h. (C) Nuclear extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting for RelA/p65 and Lamin B levels. Bars indicate mean ± SEM (n = 3) for each condition, and were analyzed by ANOVA. (D) Total cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot to determine the phosphorylation status of cofilin1 at Ser3. Total levels of cofilin1 were used to monitor protein loading. Bars indicate mean ± SEM (n = 3) for each condition, and were analyzed by ANOVA. (E) Cells were fixed and stained with Phalloidin-488 (green) to mark actin filaments and DAPI (blue) to mark nuclei. Each image is representative of three experiments. (F) Mean fluorescence intensity of actin stress fibers (phalloidin staining)/cell was determined by analyzing 35-39 cells. Values are reported in arbitrary units (AU), and were analyzed by ANOVA.