Figure 3.
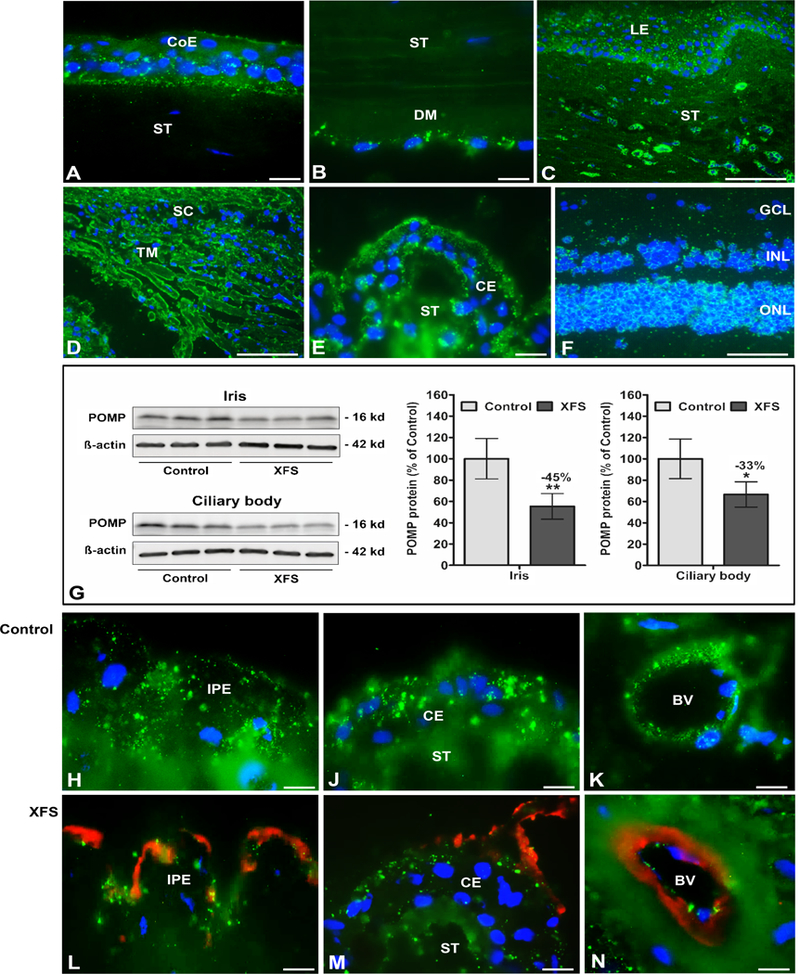
Expression of POMP protein in ocular tissues of normal human donor eyes and donor eyes with XFS, as determined by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Immunofluorescence labelling of normal eye tissues shows punctate POMP immune-positivity (green fluorescence) in the cytoplasm of the corneal epithelium (A), the corneal endothelium (B), limbal epithelium and stromal cells (C), trabecular meshwork endothelium (D), ciliary epithelium (E), and retinal cell layers (F).
Reduced POMP protein expression levels in iris and ciliary body tissues of XFS eyes compared to age matched controls are shown by Western blot analysis (G), and by immunofluorescence labelling of iridal (H,L) and ciliary epithelia (J,M) as well as vascular endothelia in the iris (K,N). Reduced staining intensity in XFS tissues is associated with LOXLI-positive exfoliation material accumulations (red immunofluorescence) on the surface of the iris pigment epithelium (L), ciliary epithelium (M) and iris blood vessel walls (N). Western blot (cropped images) and densitometry analysis shows reduced POMP protein expression in iris and ciliary body tissue lysates of XFS eyes compared to control eyes (G). Data are shown as the POMP/B-actin ratio (n=6 for each group; mean ± standard deviation; *P<0.01; **P<0.005); uncropped versions of all Western blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 16. (BV blood vessel, CE ciliary epithelium, CoE corneal epithelium, DM Descemet membrane, GCL retinal ganglion cell layer, INL inner nuclear layer, IPE iris pigment epithelium, LE limbal epithelium, ONL outer nuclear layer, SC Schlemm’s canal, ST stroma, TM trabecular meshwork; DAPI nuclear counterstain in blue; scale bars = 100 μm in C,D,F and 20 μm in A,B,E,H-N).
