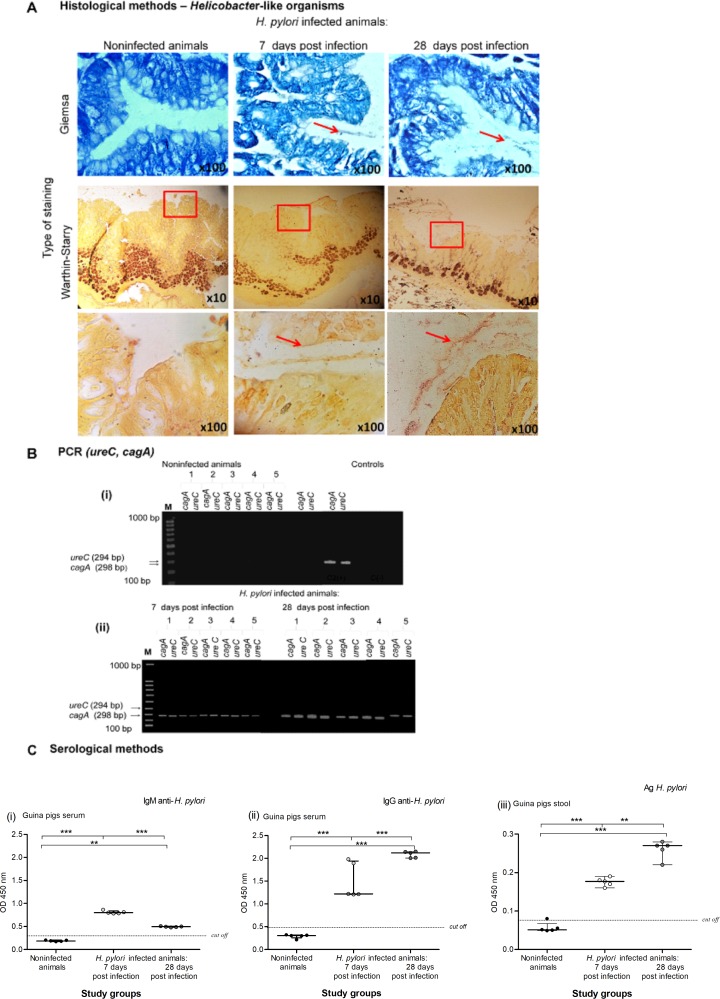
Fig 1. Histological, serological and molecular assessment of H. pylori infection in an experimental guinea pig model.
(A) Representative images of gastric tissue sections collected from guinea pigs noninfected or infected with H. pylori after 7 and 28 days from inoculation, stained with Giemsa and Warthin-Starry method and visualized in a light microscope (YS100, Nikon, Japan). Red arrows and squares indicate the location of Helicobacter-like organisms (HLO). (B) The electrophoretic separation of the ureC and cagA H. pylori gene amplification products by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of gastric tissue samples isolated from noninfected or H. pylori infected guinea pigs after 7 days from inoculation. Samples were run in 1.4% agarose gel in the presence of marker size (M) 100bp and controls: (C [+]—positive control—H. pylori DNA isolated from H. pylori suspension at the density 1x108 CFU/ml, C [–]—negative control, reaction mixture lacking DNA). (i) Lack of amplification products for cagA and ureC genes in the gastric tissue samples isolated from control animals. (ii) Presence of DNA (amplification products) for CagA (the cagA gene—298 bp) and UreC (the ureC gene amplification—294 bp) in the gastric tissue samples isolated from animals infected with H. pylori. (C) Serological methods for detection of the serum level of anti-H. pylori IgM (i), anti-H. pylori IgG (ii) and H. pylori antigens (iii) in stool samples collected from guinea pigs noninfected or infected with H. pylori after 7 and 28 days from inoculation. Five animals per group for control and, 5 per group for infected animals (7 and 28 days after inoculation, 5+5) were examined. The results are presented as median values of four independent experiments performed in triplicates for each experimental variant. Statistical analysis was performed with the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test. Statistical significance *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 was obtained for H. pylori infected animals (7 and 28 days after inoculation) vs control animals; H. pylori infected animals 7 days vs animals 28 days from the last inoculation.