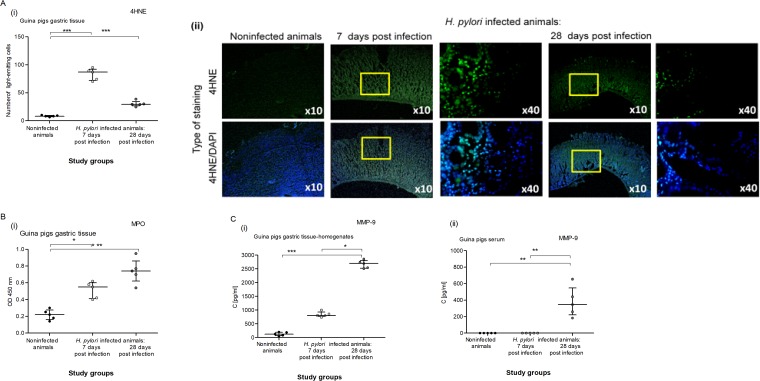
Fig 3. Detection of 4HNE, MPO and MMP-9 in the gastric tissue of H. pylori infected guinea pigs.
(A) Oxidative stress assessment in the gastric tissue of guinea pigs noninfected or infected with H. pylori after 7 and 28 days from inoculation based on the presence of 4-hydroxynonenal (4HNE). (i) Fluorescence intensity of 4HNE in the gastric tissue measured using the Image J software version 1.48v (National Institute of Health, United States). (ii) Representative images of 4HNE in the gastric tissue visualized in a confocal microscope (LeicaTCS SP) at wavelengths: FITC 495 nm excitation and 519 nm emission; DAPI 345 nm excitation and 455 nm emission. (B) Level of myeloperoxidase (MPO) in the gastric tissue homogenates of guinea pigs noninfected or infected with H. pylori after 7 and 28 days from inoculation. (C) Level of metalloproteinase (MMP-9) in gastric tissue homogenates (i) or serum (ii) of guinea pigs noninfected or infected with H. pylori after 7 and 28 days from inoculation. Five animals per group for control and, 5 animals per group for infected individuals (7 and 28 days after inoculation, n = 5+5) were examined. The results are presented as median values with a range of four independent experiments performed in triplicates for each experimental variant. Statistical analysis was performed with the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test. Statistical significance *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 was obtained for H. pylori infected animals (7 and 28 days after inoculation) vs control animals; H. pylori infected animals 7 days vs animals 28 days from the last inoculation.