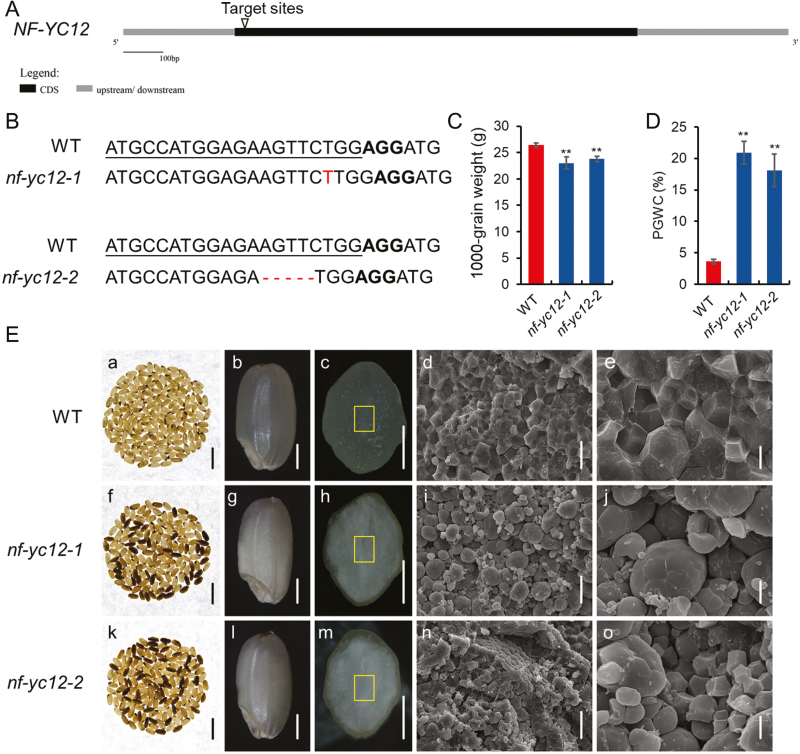
Fig. 2.
Rice nf-yc12 knockout mutants generated by CRISPR/Cas9 and their phenotypes. (A) Schematic diagram of the genomic region of NF-YC12 and the sgRNA target site. (B) Mutation sites in nf-yc12-1 and nf-yc12-2, as compared with wild-type (WT) sequences. The target sites are underlined, protospacer-adjacent motif sequences are shown in bold, and inserted or deleted nucleotides are indicated in red. (C) Thousand-grain weights and (D) percentage of grains with chalkiness (PGWC) of WT and nf-yc12 seeds. Data are means (±SD) from three replicates, each of which included at least 200 seeds. Significant differences between the WT and the mutants were determined using Student’s t-test (**P<0.01). (E) Phenotypes of seeds of the WT and nf-yc12 mutants. (a, f, k) Images of 200 grains of mature seeds; scale bars are 10 mm. (b, g, l) Appearance of mature seeds; scale bars are 1 mm. (c, h, m) Cross-sections of mature seeds; scale bars are 1 mm. (d, e, i, j, n, o) SEM images of the central area of mature endosperm at different magnifications: the areas are indicated by the squares in (c, h, m). Scale bars are 20 μm (d, i, n), 5 μm (e, j, o).