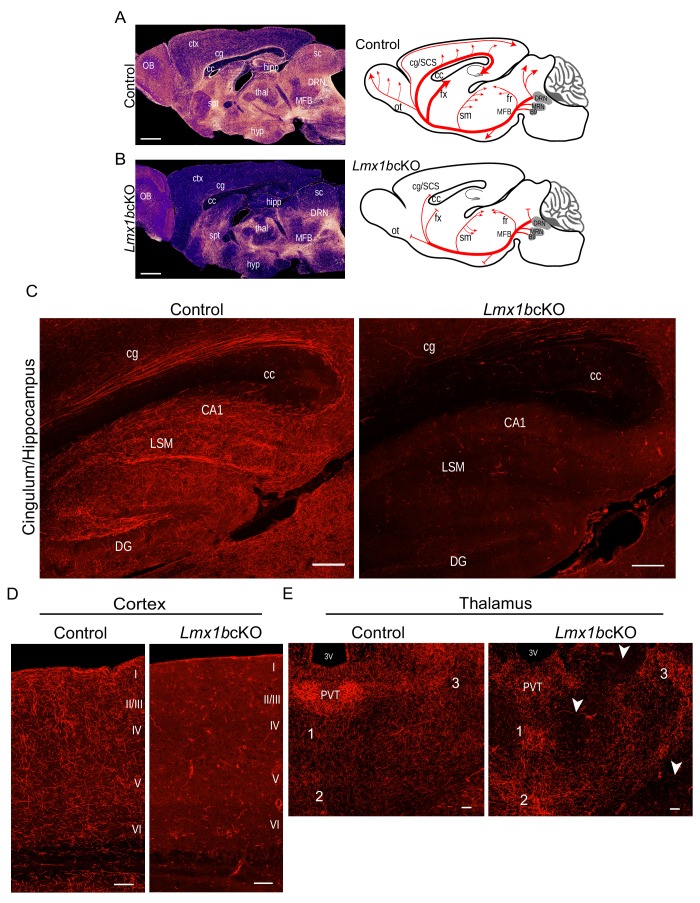
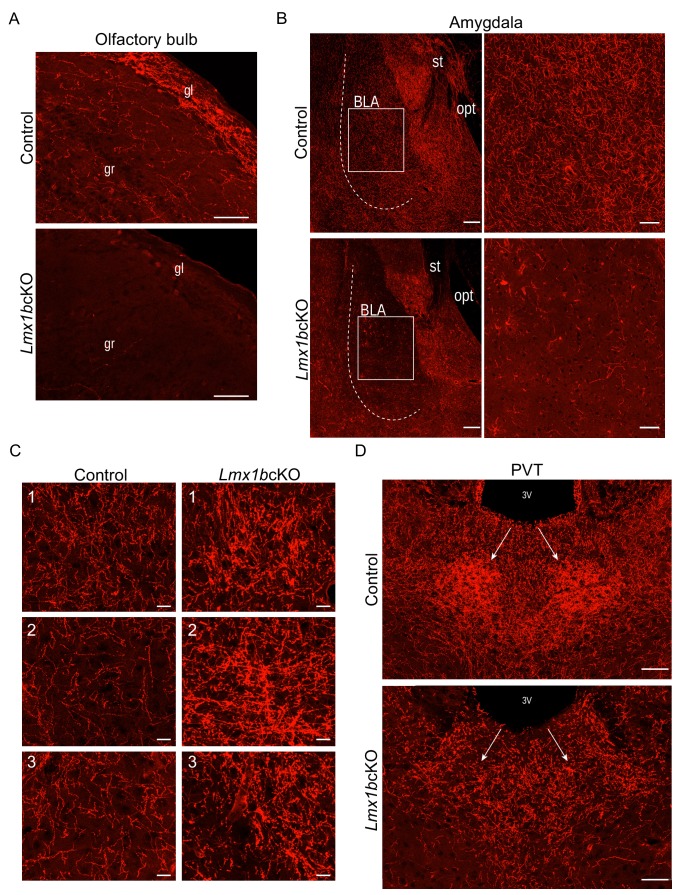
Figure 1. Lmx1b is required for the formation of ascending 5-HT axon projection pathways.
(A, B) Ascending 5-HT axonal projection system immunolabeled using an anti-RFP antibody to TdTomato in whole sagittal forebrain sections of 3 month old mice displayed by heatmap. Lmx1bcKO TdTomato+ axons were nearly absent in numerous brain regions (B) compared to controls (A) (n = 6, controls; n = 7, Lmx1bcKO adult mice). Right, schematics depicting 5-HT axon trajectories in Lmx1bcKO vs. control brains. Scale bars, 1000 µm. OB, olfactory bulb; ctx, cortex; cg, cingulum; cc, corpus callosum; hipp, hippocampus; spt, septum; hyp, hypothalamus; thal, thalamus; sc, superior colliculus; MFB, medial forebrain bundle; DRN, dorsal raphe nucleus. Schematic (right): ot, olfactory tract; cg/SCS, cingulum/supracallosal stria; fx, fornix; sm, stria medularis; fr, fasciculus retroflexus. (C) Confocal images of TdTomato+ axons in sagittal sections. Lmx1bcKO axons failed to fill cingulum bundles or innervate the hippocampus. Scale bars, 200 µm. cg, cingulum; cc, corpus callosum; LSM, lacunosum moleculare; DG, dentate gyrus; CA1 of hippocampus. (D) Coronal sections of cortex show near complete lack of Lmx1bcKO TdTomato+ axons Scale bars, 50 µm. (E) Coronal view of altered patterns of TdTomato+ axons in Lmx1bcKO thalamus. Arrowheads indicate areas devoid of axons in Lmx1bcKO thalamus. Numbers correspond to areas of axon clumping in Lmx1bcKO thalamus. See Figure 1—figure supplement 2 for high magnification images. Scale bars, 100 µm. PVT, paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus; 3V, third ventricle.