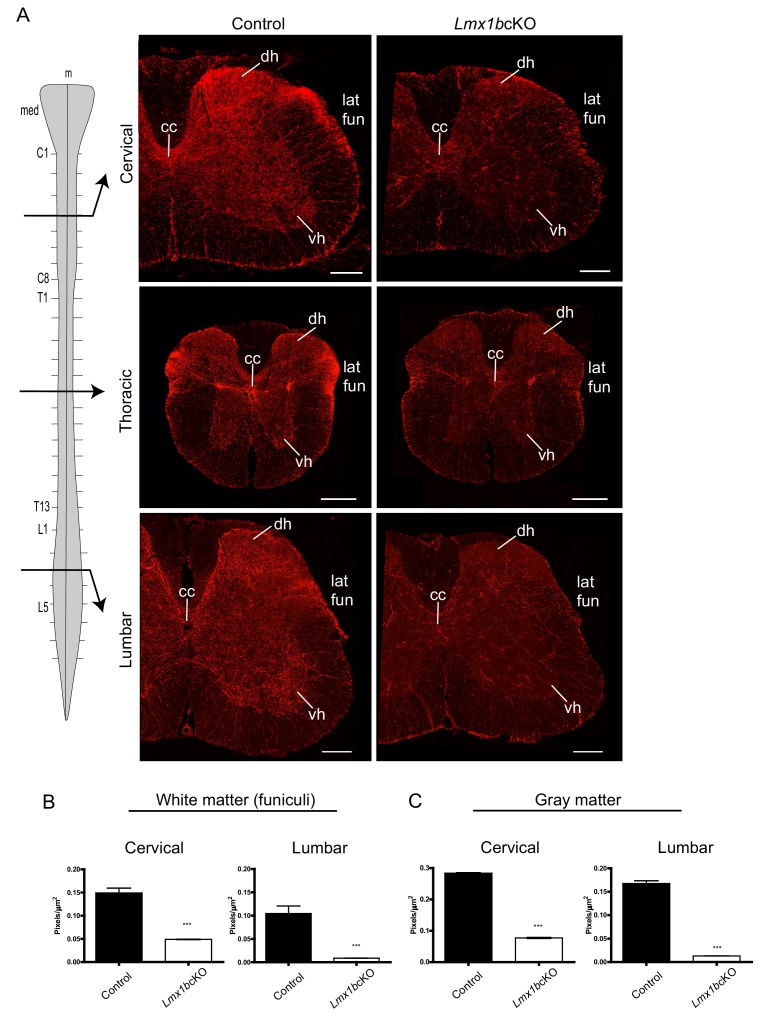
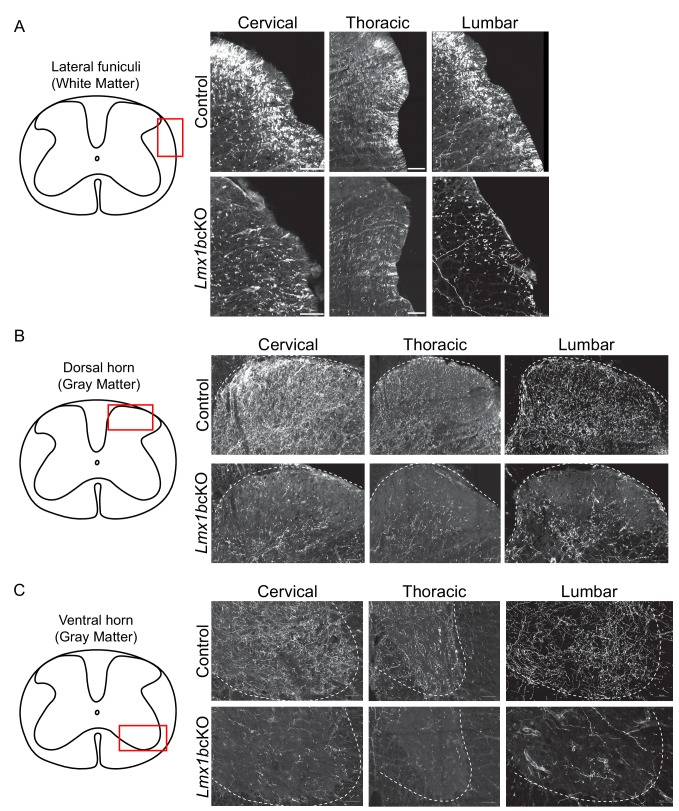
Figure 2. Lmx1b is required for the formation of descending 5-HT axon projection pathways.
(A) Coronal sections taken at cervical (C4), thoracic (T6), and lumbar (L3) levels of the spinal cord (diagram, left). Immunolabeling for TdTomato shows Lmx1bcKO axons were severely reduced at every level of the cord in both gray and white matter compared to controls. Scale bars, 200 µm. m, midline; med, medulla; cc, central canal; dh, dorsal horn; vh, ventral horn; lat fun, lateral funiculi. (B, C) Quantification of total TdTomato+ axons (pixels/µm2) in white (B) and gray (C) matter at cervical and lumbar levels (n = 3, control; n = 3 Lmx1bcKO mice). Two-way ANOVA with Welch’s correction, *p<0.05, **p<0.001, and ***p<0.0001. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.