Figure 3:
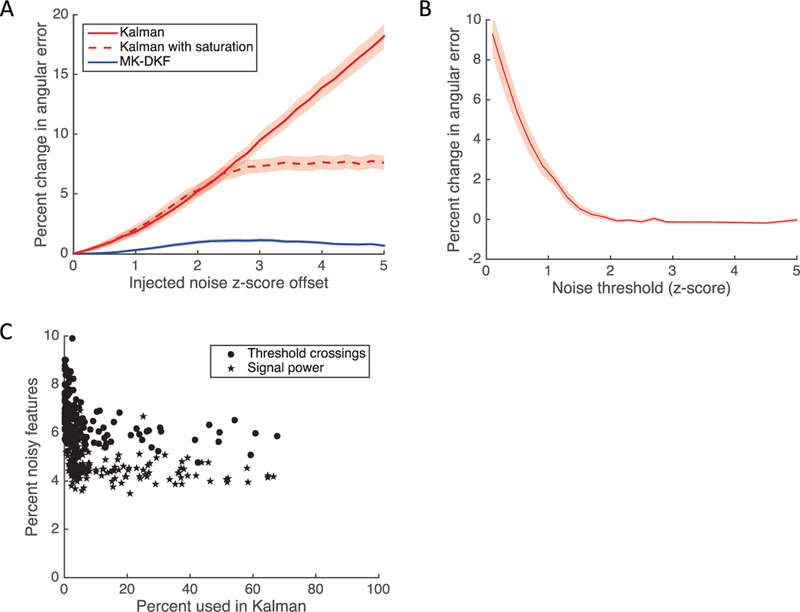
(A) Change in angular error as a function of z-score offset for the Kalman filter, the Kalman filter with feature saturation, and MK-DKF decoders. We identified 96 research sessions where T10 performed closed-loop neural control. For each session, we performed a 50–50 split of the data and used the training data to compute the coefficients for the decoders; then we predicted the angular error on the testing data. Next, we added a z-score offset to a single channel (standardized for each decoder). The shaded areas represent the standard error of measurement for each decoder. (B) Change in angular error as a function of feature thresholding. During the bootstrapping procedure, we saturated features for both the training and testing data sets and computed the change in angular error compared to no saturation. The shaded area represents the standard error of measurement. (C) Examining the frequency of noise events. For each of the bootstrapped simulations, we counted the frequency at which each feature was incorporated into the decoder (m = 40), as well as the frequency at which the feature was observed to deviate by more than two z-scores.
