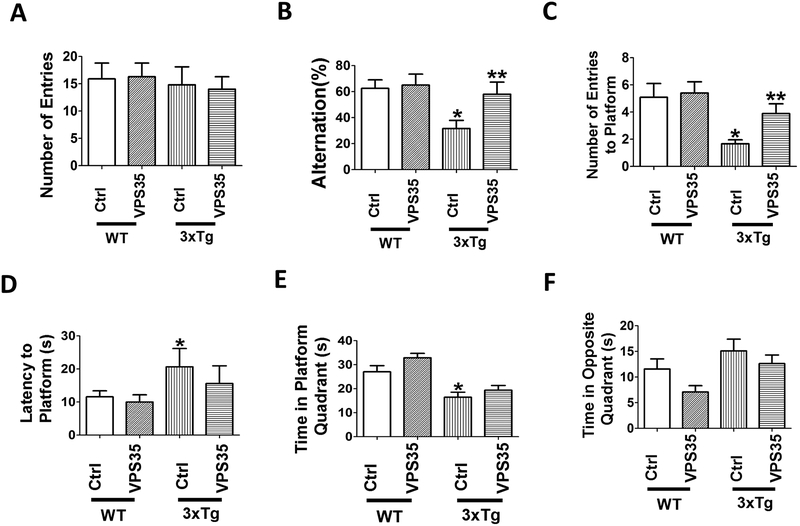
Figure 1. VPS35 gene transfer rescues behavioral deficits of 3xTg mice.
(A) Number of total arm entries for 3xTg mice (3xTg) and wild‐type mice (WT) treated with AAV‐VPS35 (VPS35) or AAV‐empty vector control (Ctrl). (B) Percentage of alternations between 3xTg and WT mice receiving AAV‐VPS35 or AAV‐empty vector (*p<0.05). (C) Morris water maze, probe trial for the same four groups of mice, number of entries to the platform area; (D) latency to first entry to the platform area; (E) time spent in the platform quadrant; (F) time spent in the opposite quadrant. Values represent mean ± standard error of the mean (*p<0.05). (WT-Ctrl: n=11; WT‐VPS35: n =10; 3xTg-Ctrl, n=8; 3xTg-VPS35, n=8).