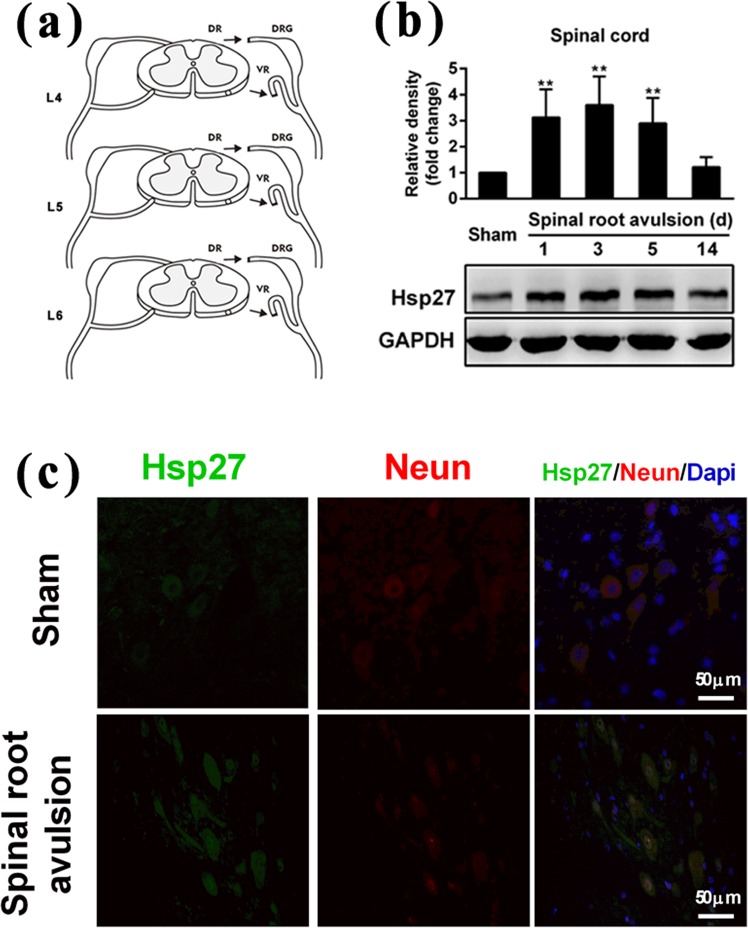
Figure 1.
Effects of lumbosacral nerve root avulsion on the expression of Hsp27 protein in neurons of the anterior horn of the spinal cord. (a) Images of the procedure of lumbosacral nerve root avulsion injury in rats. Arrowheads indicate the injury site in the spinal cord (LNRA, lumbosacral nerve root avulsion; DR, dorsal root; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; VR, ventral root). (b) After the LNRA models of rats were established for 1, 3, 5, and 14 days, the Hsp27 protein level was detected by western blotting analysis in L4–L6 spinal cord tissue of the sham group (N = 4) and LNRA groups (N = 4). GAPDH was used as a loading control for western blotting. Hsp27 protein expression was quantified by densitometric analysis. (c) After LNRA injury for 3 days, Hsp27 (Green), NeuN (Red), and Dapi (Blue) were assessed by immunofluorescence staining in L4–L6 spinal cord tissue of the sham and LNRA groups. The representative image of neurons of the anterior horn of the spinal cord was shown. Scale bar, 50 μm. The results were expressed as fold change compared to the sham group. Each bar represents the mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 versus the sham group.