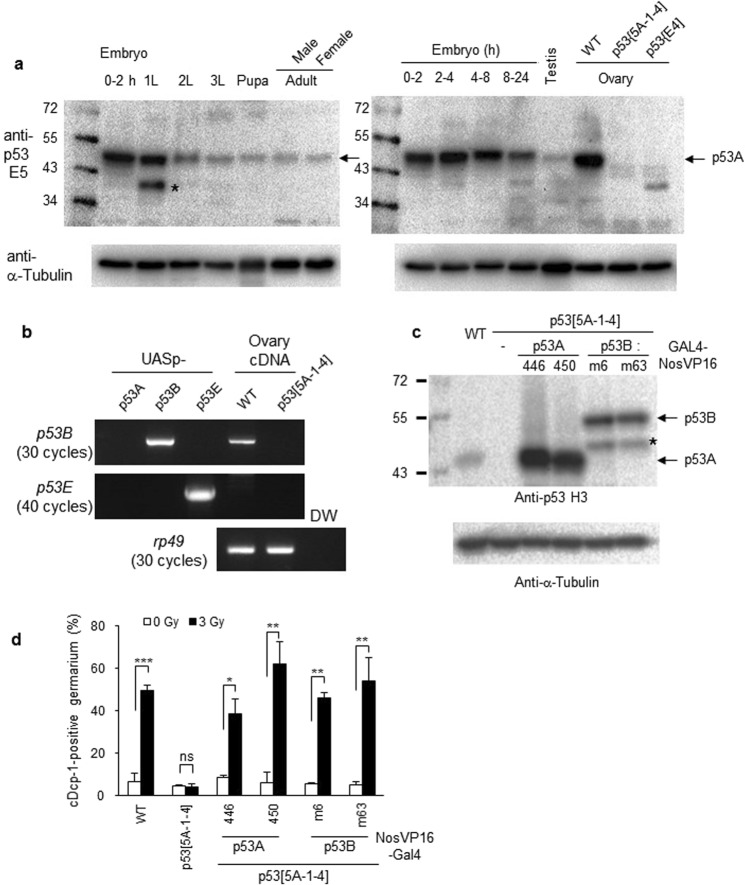
Figure 3.
Expression of p53A and p53B can rescue IR-induced germline cell death in the p53 mutant germarium. (a) Lysates were generated from the embryos of the indicated ages, first, second, third instar larvae (1 L, 2 L, and 3 L), pupae, adult males and females, and testis and ovaries from the wild type or p53 mutants. The monoclonal antibody E5, which recognizes p53A, p53B and p53E was used. Bands corresponding to the p53A isoform are indicated by an arrow. Other bands, including the ones indicated by asterisks, appear to be a non-specific or degradation product of p53 protein. The membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti-α-Tubulin as a loading control. (b) To determine expression levels of the p53B and p53E transcripts, reverse-transcription PCR analysis was performed using total RNA preparation from ovaries of wild type and p53 mutant flies. UASp constructs containing the cDNA of each p53 isoform were used as controls. (c) Western blot of ovaries from wild type or transgenic flies expressing the indicated p53 isoform in the p535A-1-4 mutant. Two independent UASp-p53 insertion lines (446 and 450 for p53A, m6 and m63 for p53B) were used for each isoform. The blot was probed with anti-p53 H3 antibody followed by anti-α-Tubulin antibody. The band corresponding to each isoform is indicated. A signal indicated with * may be a degradation product of p53B isoform. (d) Transgenic lines expressing each p53 isoform in the p535A-1-4 mutant germline cells were tested for IR-induced cell death in the germarium by staining with antibody against cleaved Dcp-1 (cDcp-1). The values are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (ns p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001). At least 200 germariums in total were counted for each sample except for p53A(450) rescued flies (48 and 76 germariums for 0 Gy and 40 Gy, respectively). Uncropped gels and blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. S5.