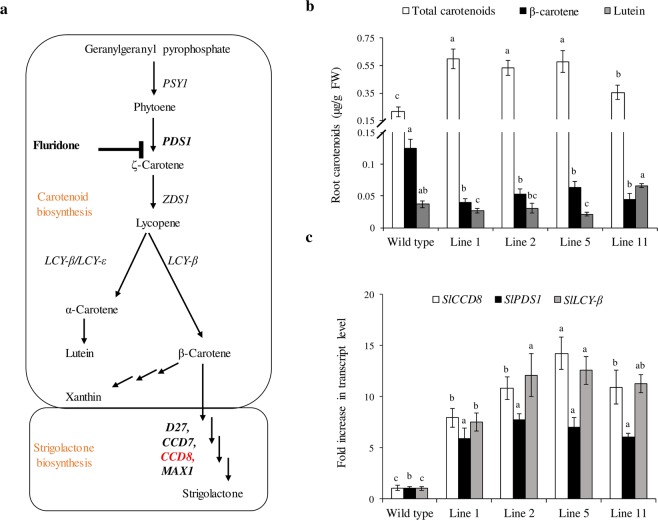
Figure 6.
Carotenoid-biosynthesis pathway, carotenoid contents and transcript expression of three candidate genes (SlCCD8, SlPDS1 and SlLCY-β) in CCD8Cas9 mutants. (a) Schematic representation of carotenoid-biosynthesis pathway leading to β-carotene formation and strigolactone biosynthesis. Target site for fluridone shown by blunt black arrow. Enzymes are aligned with arrows. The enzymes belonging to carotenoid biosynthesis are: phytoene synthase (PSY1); phytoene desaturase (PDS1); ζ-carotene desaturase (ZDS1), lycopene ɛ-cyclase (LCY-ε); lycopene β-cyclase (LCY-β). The enzyme belongs to SL biosynthesis are D27, carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases 7, 8 and MAX1. (b) Carotenoid content in tomato roots of control and CCD8Cas9 mutant plants. Values are based on the analysis of 3 months old plants grown in green house, bars represent the average of two experiments, was done with the pooled sample from two independent plant roots for each line ± SE. Statistical differences between the wild-type control were calculated with Student’s t-test (P < 0.05). Different small letter on bar indicate a significant difference between the CCD8Cas9 edited lines and the WT plants. (c) Quantification of SlCCD8, SlPDS1 and SlLCY-β transcript levels in roots of CCD8Cas9 edited lines and wild type (WT) plants using quantitative real-time PCR. Expression level of transcript was displayed after normalization with internal control tomato elongation factor-1α (EF1-α). Bars with different letters are significantly different from each other (student t-test at p < 0.05 when compared with the controls). Results represent the average of at least three independent experiments with three technical repeat ± SE (n = 3), and expressed as fold increase in expression of transcripts relative to the control plants.