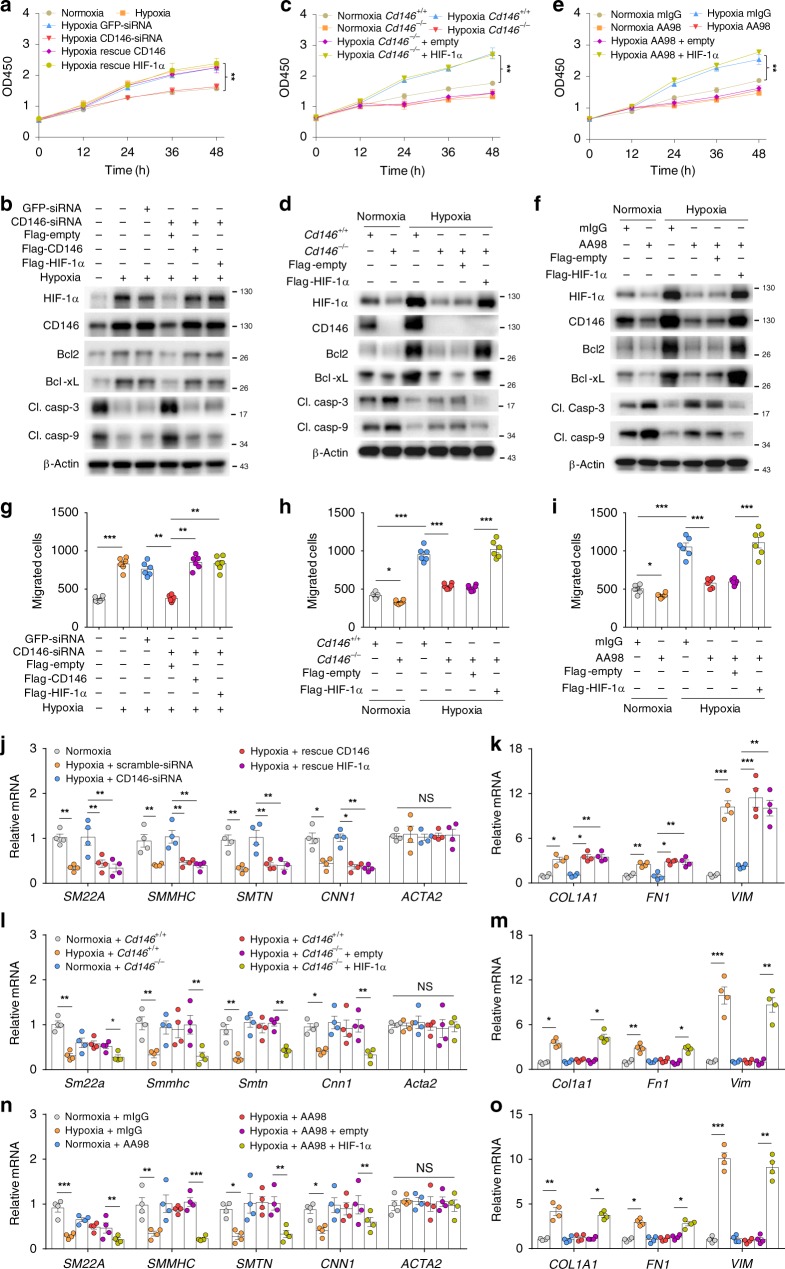
Fig. 4.
CD146-HIF-1α axis promotes a synthetic phenotype in PASMCs. a–d Human a, b or mouse c, d PASMCs were transfected as indicated, and cultured under normoxic or hypoxic conditions, and cell proliferative ability and expression of indicated proteins were determined by CCK-8 assay a, c or WB b, d. e, f Human PASMCs were cultured under normoxic or hypoxic conditions in the presence of anti-CD146 AA98 or control mIgG (50 μg/ml). The cell proliferative ability and the expression of indicated proteins were determined by CCK-8 assay e or WB f. g, h Human g or mouse h PASMCs were transfected as in a or c. Cell migration was measured in a Transwell Boyden chamber. i Human PASMCs were treated as in e. Cell migration was measured in a Transwell Boyden chamber. j–m Human j, k or mouse l, m PASMCs were transfected as in a or c. The mRNA levels of contractile j, l and synthetic markers k, m were detected by real-time RT-PCR. n, o PASMCs were treated as in e. The mRNA levels of contractile n and synthetic markers o were detected by real-time RT-PCR. n = 4 j–o or n = 6 a, c, e, g–i biological replicates for each group. All WB represent data from three b, d, f independent experiments. In all statistical plots, the results are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. n.s., not significant; by two-tailed Student’s t test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file