Figure 1.
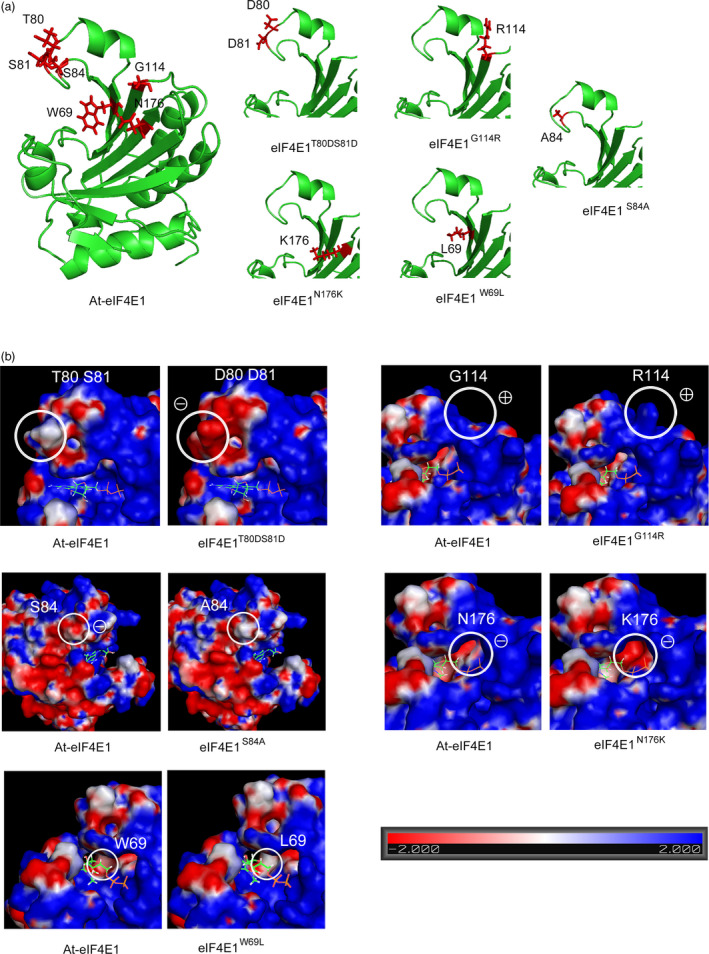
Three‐dimensional analysis of the eIF4E1 proteins encoded by the five constructed alleles eIF4E1 W69L , eIF4E1 T80 DS 81D , eIF4E1 S84A , eIF4E1 G114R and eIF4E1 N176K . (a) Three‐dimensional homology modelling of the Arabidopsis eIF4E1 protein, based on crystallography data from the Pisum sativum eIF4E 3D structure (PDB ID: 2WMC‐C), for the wild‐type (WT) and the five constructed alleles. The positions of the six amino acids to be introduced are indicated in red along with their side chains. (b) Electrostatic potential of the surface of eIF4E1 proteins compared to the WT. Positions of the amino acid substitutions are circled on the WT protein (left panel) and on the mutated proteins (right panel). To indicate the cap‐binding pocket, a 7‐methyl‐GDP molecule is shown in its binding conformation to the eIF4E protein.
