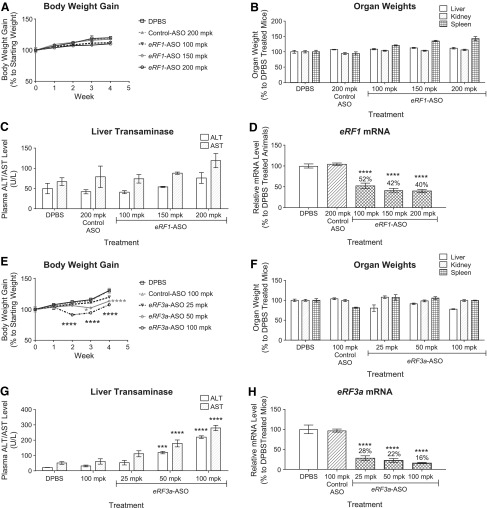
FIG. 1.
Reduction of eRF1 to ∼40% and eRF3a to ∼30% of normal levels in mouse liver is well tolerated. (A–D) Male C57BL/6 mice 7 weeks of age (n = 4) were treated with eRF1-ASO at 100, 150, or 200 mg/kg/week. DPBS and a scrambled ASO dosed at 200 mg/kg/week were used as controls. Animals were dosed twice a week for a total of eight doses in a 4-week period. Necropsy was performed 48 h after the last dose of ASO. Results are presented as mean ± standard error. (A) Body weights measured once a week. (B) Liver, kidney, and spleen weights measured at necropsy. (C) Plasma ALT and AST levels measured by clinical analyzer at the time of necropsy. (D) qPCR analysis of eRF1 mRNA levels in mouse liver samples. Mouse Gapdh mRNA was used as endogenous control. eRF1 mRNA level in DPBS-treated animals was set as 100%. (E–H) Male C57BL/6 mice 7 weeks of age (n = 4) were treated with eRF3a-ASO at 25, 50, or 100 mg/kg/week. DPBS and a scrambled ASO dosed at 100 mg/kg/week were used as controls. Animals were dosed twice a week for a total of eight doses in a 4-week period. Necropsy was performed 48 h after the last dose of ASO. Results are presented as mean ± standard error. (E) Body weights measured once a week. (F) Liver, kidney, and spleen weights measured at necropsy. (G) Plasma ALT and AST levels measured by clinical analyzer at the time of necropsy. (H) qPCR analysis of eRF3a mRNA levels in mouse liver samples. Mouse Gapdh mRNA was used as endogenous control. eRF3a mRNA level in DPBS-treated animals was set as 100%. Statistical significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA and Dunnett's multiple comparison test in Prism. All groups were compared with DPBS-treated group. ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. mpk, mg/kg/week; ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase; eRF, eukaryotic release factor; mRNA, messenger RNA; qPCR quantitative polymerase chain reaction; DPBS, Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline; ANOVA, analysis of variance.