Figure 10.
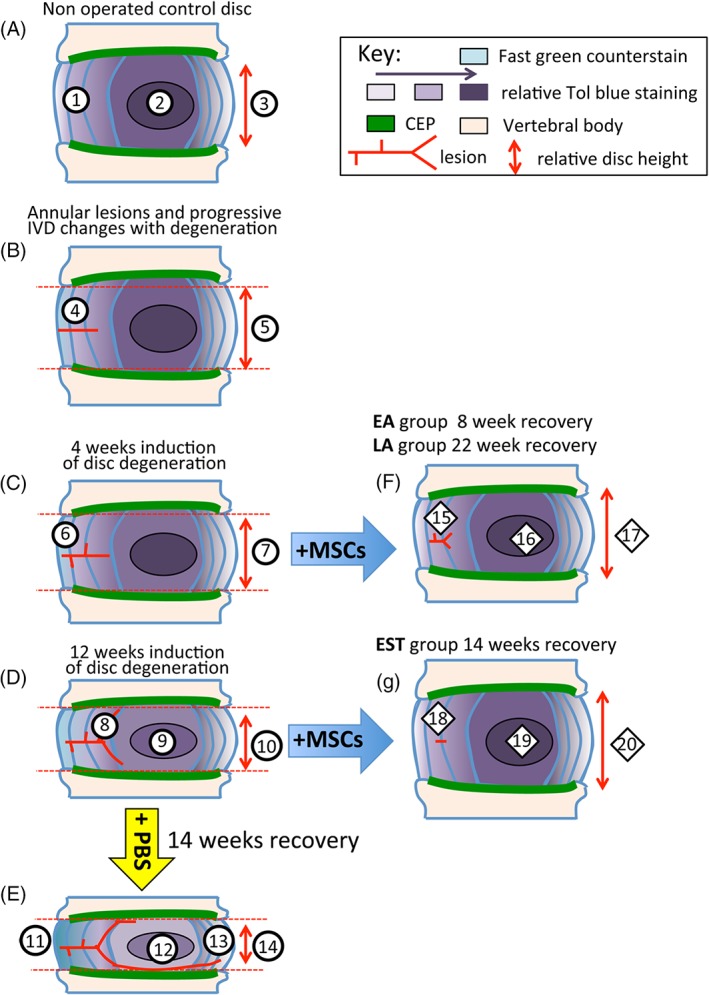
Diagrammatic depiction of sheep IVDs undergoing degeneration and recovery following MSC administration. (A) Control NOC disc, (B) establishment of lesion, (C) changes to IVD and lesion site 4 weeks after induction of disc degeneration. (D) Changes to IVD and lesion site 12 weeks after induction of disc degeneration. (E) Further progression of disc degeneration and lesion development after injection of PBS carrier after 14 weeks recovery. (F) Reversal of degenerative features by MSCs in IVDs of EA and LA treatment groups. (G) Reversal of degenerative features by MSCs in IVDs in EST treatment group. EA, early Acute; LA, Late Acute and EST, established treatment group; NOC, nonoperated control. Explanation of labeled features. Typical features of a normal nonoperated control (NOC) IVD. (1) Normal AF containing a gradient of toluidine blue staining. (2) Localization of toluidine blue staining in the nucleus pulposus (NP). (3) Normal disc height. Progressive features evident as IVDs undergo degeneration induced by a controlled annular defect. (4) Establishment of the controlled outer annular surgical defect. (5) Slight reduction in disc height. (6) After 4 weeks induction of disc degeneration de‐lammellations are generated by the defect. (7) Further reduction in disc height with advancing disc degeneration and decreased toluidine blue staining in the NP. (8) Bifurcation of the defect in the inner AF. Focal proteoglycan loss along the tract of the lesion in the outer AF. (9) Further reduction in toluidine blue staining in the NP. (10) Further reduction in the disc height at 12 weeks induction of disc degeneration. Features in IVDs which received injection of PBS carrier rather than MSCs resulting in degenerative changes in the IVD over the next 14 weeks. (11) Thickening of outer AF lamellae devoid of proteoglycan staining but loss of normal lamellar organization. (12) Reduction in the proteoglycan content of the NP. (13) Propagation of the outer annular defect towards the contralateral AF. (14) Significant reduction in disc height. Reparative changes in IVDs induced by intradiscal administration of MSCs into IVDs that had undergone disc degeneration for 4 weeks after 8 or 22 weeks recovery with MSCs. (15) Significant reduction in lesion size with a residual lesion still evident. Repair of the outer AF. (16) Proteoglycan content of the NP largely replenished. (17) Recovery of close to normal IVD heights similar to NOC IVDs. Reparative changes in IVDs induced by intradiscal administration of MSCs into IVDs that had undergone degeneration for 12 weeks and had a 14 week recuperative period. (18) Recovery of AF proteoglycan levels, almost complete disappearance of annular lesion. (19) Recovery of normal proteoglycan levels in NP. (20) Re‐attainment of normal disc height
